-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 159
A Walkthrough the Code
This wiki page is a starting point for anyone that is interested in understanding how c2go works internally or are interested in learning the code base to work on issues.
This page is still a work in progress.
The basic process is this:
- The
clangprogram preprocesses the C input file and produces a temporary file,/tmp/pp.c. This file contains a lot more source code because all the of the#includedirectives have been evaluated. - The
clangprogram is used again to parse thepp.cfile and produce an AST. This is the coloured output you will see below. - The
clangoutput (which is text) is converted by theastpackage into a real AST. - The
transpilerpackage converts the AST into Go's internal AST. - The Go AST is rendered into Go code.
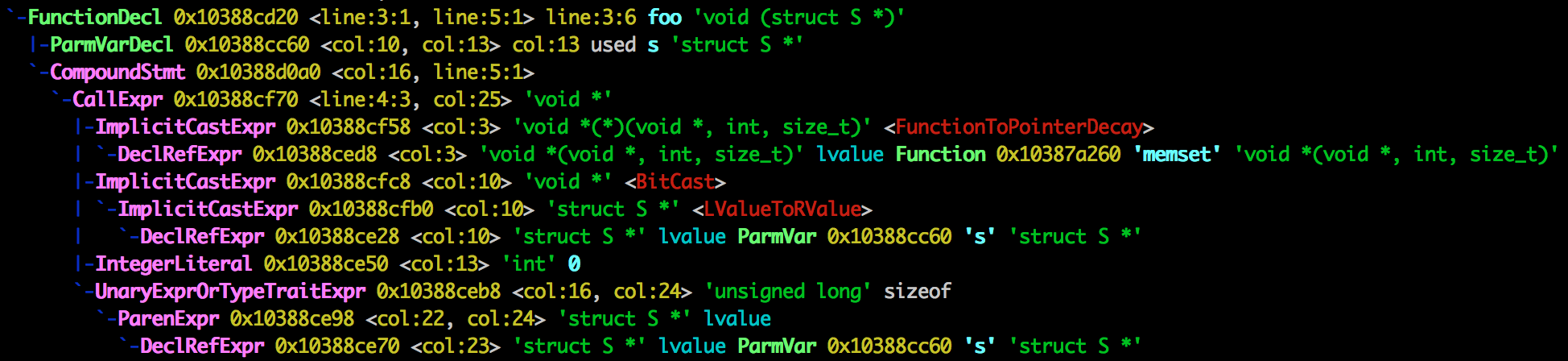
The clang program parses C and produces text that represents the internal clang AST, here is an example of the output:
Random notes:
This text (once the colours have been removed) ...
The first thing to understand is where the input is coming from. c2go does not parse the C code itself, instead it uses clang to parse the C and output an AST. The AST describes C code in a machine readable format.
C2go reads this input and translates the text into its own structure.
The AST is then transpiled into a Go AST.
The Codebase Documentation can be found here.
- ast - contains the code for parsing the clang AST output and building the AST that will be transpiled. Each file in the package represents a different AST node and has an associated test file.
- darwin
- linux
- noarch
- transpiler
- util