链表相关的核心点
- null/nil 异常处理
- dummy node 哑巴节点
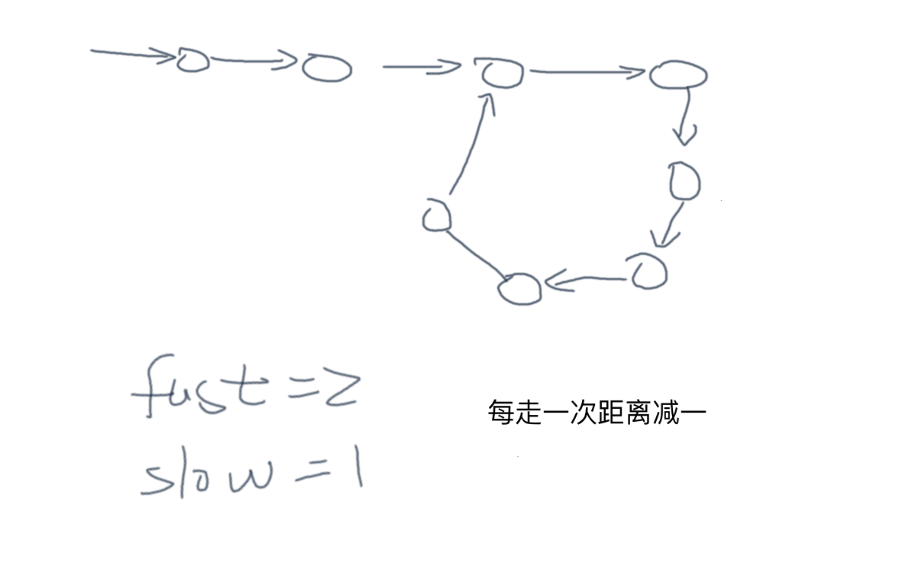
- 快慢指针
- 插入一个节点到排序链表
- 从一个链表中移除一个节点
- 翻转链表
- 合并两个链表
- 找到链表的中间节点
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
public class ListNode {
public var val: Int
public var next: ListNode?
public init(_ val: Int) {
self.val = val
self.next = nil
}
}
class Solution {
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/solution/swift-bian-li-tong-shi-shan-chu-lian-biao-zhong-fu/
func deleteDuplicates(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var current = head
while let now = current,let next = now.next{
if now.val == next.val {
now.next = next.next
}else{
current = now.next
}
}
return head
}
}给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现的数字。
思路:链表头结点可能被删除,所以用 dummy node 辅助删除
public class ListNode {
public var val: Int
public var next: ListNode?
public init(_ val: Int) {
self.val = val
self.next = nil
}
}
class Solution {
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/solution/swift-shuang-zhi-zhen-lian-biao-bian-li-tou-bu-tia/
func deleteDuplicates(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
let top = ListNode(0)
top.next = head
var prev = top
var current = head
while let now = current, var next = now.next {
if now.val == next.val{
//求出next指向最后一个相等的
while let end = next.next{
if now.val == end.val {
next = end
}else{
break
}
}
prev.next = next.next
current = next.next
}else{
prev = now
current = next
}
}
return top.next
}
//递归实现
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/solution/swift-di-gui-shi-xian-by-hu-cheng-he-da-bai-sha/
func deleteDuplicates(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var res = head
if let current = res,let next = current.next{
if current.val == next.val{
var end : ListNode? = next
while end != nil && current.val == end!.val {
end = end!.next
}
res = deleteDuplicates(end)
}else{
current.next = deleteDuplicates(next)
}
}
return res
}
}注意点 • A->B->C 删除 B,A.next = C • 删除用一个 Dummy Node 节点辅助(允许头节点可变) • 访问 X.next 、X.value 一定要保证 X != nil
反转一个单链表。
思路:用一个 prev 节点保存向前指针,temp 保存向后的临时指针
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/solution/swift-shuang-zhi-zhen-bian-li-by-hu-cheng-he-da-ba/
//双指针遍历
//执行用时:20 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了78.48%的用户
//内存消耗:21.7 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了25.00%的用户
func reverseList_a(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var head = head
var prev: ListNode?
while let current = head {
let next = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = head
head = next
}
return prev
}
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/solution/swift-gao-xiao-di-gui-by-hu-cheng-he-da-bai-sha/
//递归
//执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了97.24%的用户
//内存消耗:22.1 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了25.00%的用户
func reverseList(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
guard let current = head,let next = current.next else {
return head
}
let reverse = reverseList(next)
next.next = current
current.next = nil
return reverse
}反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
思路:先遍历到 m 处,翻转,再拼接后续,注意指针处理
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/solution/swift-bian-li-fan-zhuan-by-hu-cheng-he-da-bai-sha/
//遍历反转
//执行用时:12 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了38.37%的用户
//内存消耗:20.9 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func reverseBetween(_ head: ListNode?, _ m: Int, _ n: Int) -> ListNode? {
let sentry = ListNode(0)
sentry.next = head
var prev: ListNode? = sentry
var cur: ListNode? = head
//移动到反转起始位置
for _ in 1..<m{
prev = cur
cur = cur?.next
}
let beign = prev//记录反转第一个的前一个
let end = cur//记录反转的第一个
//反转m到n个元素
for _ in m...n {
let next = cur?.next
cur?.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = next
}
beign?.next = prev//重新标记反转后的头
end?.next = cur//重新标记反转后的尾
return sentry.next
}将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
思路:通过 dummy node 链表,连接各个元素
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/solution/swift-di-gui-by-hu-cheng-he-da-bai-sha/
//递归实现
//执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了94.75%的用户
//内存消耗:21.1 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func mergeTwoLists(_ l1: ListNode?, _ l2: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
let res = ListNode()
guard let cur1 = l1 else {
return l2
}
guard let cur2 = l2 else {
return l1
}
if cur1.val < cur2.val {
res.next = cur1
let next = mergeTwoLists(cur1.next,cur2)
cur1.next = next
}else{
res.next = cur2
let next = mergeTwoLists(cur1,cur2.next)
cur2.next = next
}
return res.next
}
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/solution/swift-die-dai-by-hu-cheng-he-da-bai-sha/
//迭代
//执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了94.75%的用户
//内存消耗:20.8 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func mergeTwoLists_a(_ l1: ListNode?, _ l2: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var l1 = l1, l2 = l2
let res = ListNode()
var current = res
while let cur1 = l1, let cur2 = l2 {
if cur1.val < cur2.val{
current.next = cur1
l1 = cur1.next
}else{
current.next = cur2
l2 = cur2.next
}
current = current.next!
}
current.next = l1 ?? l2
return res.next
}给定一个链表和一个特定值 x,对链表进行分隔,使得所有小于 x 的节点都在大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
思路:将大于 x 的节点,放到另外一个链表,最后连接这两个链表
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list/solution/swift-bian-li-headlian-biao-shi-shan-chu-xiao-yu-x/
//遍历head链表时,删除小于x的所有元素,同时把他们生成一个小于x的链表,最后把小于x的链表加上遍历后的head链表
//执行用时:16 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了71.00%的用户
//内存消耗:20.8 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func partition(_ head: ListNode?, _ x: Int) -> ListNode? {
let lessList = ListNode(0)//小于x的链表
var lessTail = lessList //小于x的链表的尾部
let res = ListNode(0)//原始链表的哨兵
res.next = head
var prev = res
var cur = head
while let item = cur {
if item.val < x{
prev.next = item.next
lessTail.next = item
lessTail = item
}else{
prev = item
}
cur = item.next
}
lessTail.next = res.next
return lessList.next
}哑巴节点使用场景
当头节点不确定的时候,使用哑巴节点
在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序。
思路:归并排序,找中点和合并操作
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/solution/swift-gui-bing-fei-di-gui-pai-xu-by-hu-cheng-he-da/
//归并非递归排序
//执行用时:284 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了84.55%的用户
//内存消耗:24.7 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func sortList(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
//链表不存在或长度为1直接返回
guard let item = head , item.next != nil else{
return head
}
var count = 0 //链表长度
var cur = head
while cur != nil {
count += 1
cur = cur!.next
}
let dummy = ListNode(1)
dummy.next = head
//从长度为1个元素开始合并
var length = 1
while length < count {
var begin = dummy
var index = 0
//遍历合并长度为length
while index + length < count {
var first = begin.next!,second: ListNode? = first
var firstCount = length , secondCount = length
//计算第二块的起始位置
for _ in 0..<length{
second = second?.next
}
//合并
while firstCount > 0 && secondCount > 0 && second != nil {//注意第二块长度可能小于length
if first.val < second!.val {
begin.next = first
first = first.next!
firstCount -= 1
}else{
begin.next = second
second = second!.next
secondCount -= 1
}
begin = begin.next!
}
//第一块还有剩余
while firstCount > 0 {
begin.next = first
first = first.next!
firstCount -= 1
begin = begin.next!
}
//第二块还有剩余
while secondCount > 0 && second != nil {
begin.next = second
second = second!.next
secondCount -= 1
begin = begin.next!
}
begin.next = second//指向下次合并块的开始位置
index += 2*length
}
length = 2*length
}
return dummy.next
}注意点
- 链表的递归函数调用空间复杂度:O(logn),所以必须使用非递归
给定一个单链表 L:L_→_L_→…→_L__n_→_L 将其重新排列后变为: _L_→_L__n_→_L_→_L__n_→_L_→_L__n_→…
思路:找到中点断开,翻转后面部分,然后合并前后两个链表
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list/solution/swift-zhao-dao-zhong-dian-duan-kai-fan-zhuan-hou-m/
//找到中点断开,翻转后面部分,然后合并前后两个链表
//执行用时:96 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了82.22%的用户
//内存消耗:26 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func reorderList(_ head: ListNode?) {
guard head != nil && head!.next != nil else{
return
}
//快慢指针寻找中间节点
var slow = head!, fast = head!
while fast.next != nil && fast.next!.next != nil {
slow = slow.next!
fast = fast.next!.next!
}
var head2 = slow.next
slow.next = nil
//后半段反转
var pre: ListNode? = nil
while let cur = head2 {
let next = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
head2 = next
}
head2 = pre
//拼接
let dummy = ListNode(0)
var cur = dummy
var h1 = head , h2 = head2
while h2 != nil {
cur.next = h1
let next1 = h1?.next
h1?.next = h2
h1 = next1
cur = h2!
h2 = h2?.next
}
cur.next = h1 //奇数时h1还有一个,偶数时是nil(是nil时也不影响)
dummy.next = nil
}给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
思路:快慢指针,快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减 1
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/solution/swift-kuai-man-zhi-zhen-huan-lu-jian-ce-kong-jian-/
//swift 快慢指针环路检测( 空间复杂度O(1) )
//执行用时:64 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了92.48%的用户
//内存消耗:22.2 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func hasCycle(_ head: ListNode?) -> Bool {
guard let first = head , let second = first.next else{
return false
}
var slow = first, fast: ListNode? = second
while let item = fast {
if slow === item {
return true
}
slow = slow.next!
fast = fast?.next?.next
}
return false
}给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回
null。
思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/solution/swift-kuai-man-zhi-zhen-kuai-man-xiang-yu-zhi-hou-/
//swift 快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
//执行用时:64 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了99.43%的用户
//内存消耗:22 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func detectCycle(_ head: ListNode?) -> ListNode? {
var slow = head, fast = head
while fast != nil {
slow = slow?.next
fast = fast?.next?.next
if slow === fast {
slow = head
while slow !== fast {
slow = slow?.next
fast = fast?.next
}
return slow
}
}
return nil
}请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/solution/swift-kuai-man-zhi-zhen-zhao-dao-zhong-jian-jie--2/
//快慢指针找到中间节点同时反转慢指针,之后比较前后两段(寻找中间节点判断更新)
//执行用时:112 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了97.80%的用户
//内存消耗:25.9 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func isPalindrome_a(_ head: ListNode?) -> Bool {
if head == nil {
return true
}
//快慢指针寻找中间节点,同时把前半部分反转
var slow = head, fast = head
var pre: ListNode? = nil
while fast != nil && fast?.next != nil {
let slowCur = slow
slow = slow?.next
fast = fast?.next?.next
//下面是同时反转前部分
slowCur?.next = pre
pre = slowCur
}
var head1 = pre//第一段的头
//第二段的头
var head2: ListNode? = slow
if fast != nil{//head总个是奇数时,调整第二部分头节点
head2 = slow?.next
}
while let cur1 = head1, let cur2 = head2 {
if cur1.val != cur2.val {
return false
}
head1 = head1?.next
head2 = head2?.next
}
return true
}给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。 要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
思路:1、hash 表存储指针,2、递归, 3、复制节点跟在原节点后面
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/solution/swift-die-dai-tong-bu-shen-kao-bei-by-hu-cheng-he-/
//迭代同步深拷贝
//执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了90.16%的用户
//内存消耗:22.3 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func copyRandomList(_ head: Node?) -> Node? {
var visited = [UnsafeMutableRawPointer : Node]()
func clonedNode(_ old: Node?) -> Node?{
guard let from = old else{
return nil
}
let key = Unmanaged.passUnretained(from).toOpaque()
if let item = visited[key]{
return item
}
let new = Node(from.val)
visited[key] = new
return new
}
var oldCur = head
var newCur: Node?
while let old = oldCur {
let clonedItem = clonedNode(old)
newCur?.next = clonedItem
newCur = clonedItem
newCur!.next = clonedNode(old.next)
newCur!.random = clonedNode(old.random)
oldCur = old.next
}
return clonedNode(head)
}
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/solution/swift-shen-du-bian-li-di-gui-shi-xian-by-hu-cheng-/
//深度遍历递归实现
//执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了90.16%的用户
//内存消耗:22.4 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
var visited = [UnsafeMutableRawPointer : Node]()
func copyRandomList_a(_ head: Node?) -> Node? {
guard let from = head else {
return nil
}
let key = Unmanaged.passUnretained(from).toOpaque()
if let item = visited[key]{
return item
}
let copedItem = Node(from.val)
visited[key] = copedItem
copedItem.random = copyRandomList_a(from.random)
copedItem.next = copyRandomList_a(from.next)
return copedItem
}
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/solution/swift-fu-zhi-jie-dian-gen-zai-yuan-jie-dian-hou-mi/
//swift 复制节点跟在原节点后面(空间O(1))
//执行用时:48 ms, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了90.16%的用户
//内存消耗:21.7 MB, 在所有 Swift 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
func copyRandomList_b(_ head: Node?) -> Node? {
guard head != nil else {
return nil
}
var cur = head
while let old = cur {
let copied = Node(old.val)
copied.next = old.next
old.next = copied
cur = copied.next
}
cur = head
while let old = cur {
old.next?.random = old.random?.next
cur = old.next?.next
}
cur = head
let copiedList = head!.next
var pre: Node? = nil
while let old = cur {
pre?.next = old.next
pre = old.next
old.next = old.next?.next
cur = old.next
}
return copiedList
}链表必须要掌握的一些点,通过下面练习题,基本大部分的链表类的题目都是手到擒来~
- null/nil 异常处理
- dummy node 哑巴节点
- 快慢指针
- 插入一个节点到排序链表
- 从一个链表中移除一个节点
- 翻转链表
- 合并两个链表
- 找到链表的中间节点