### Code Examples
- Sequential/Binary Search example
- JavaScript built-in findIndex(), find()
- Binary Search Tree Searches
- Depth/Breadth First Search
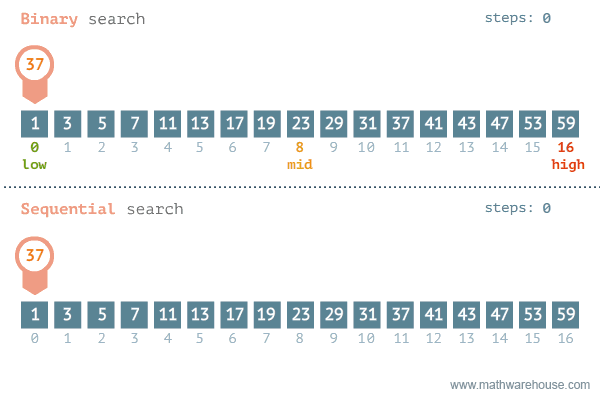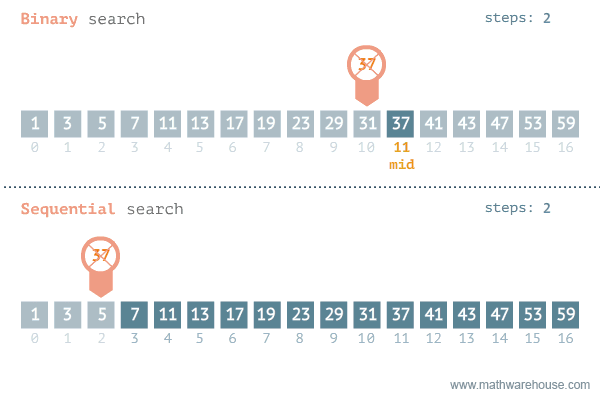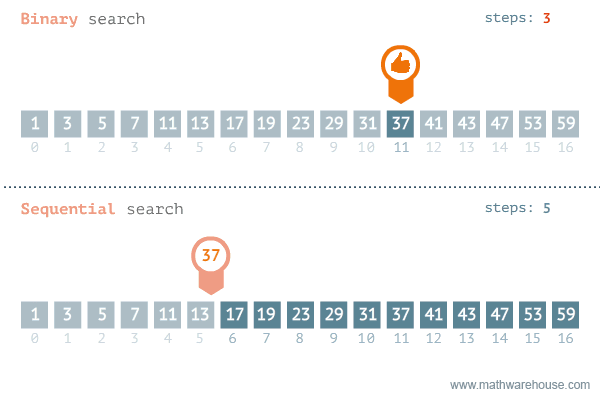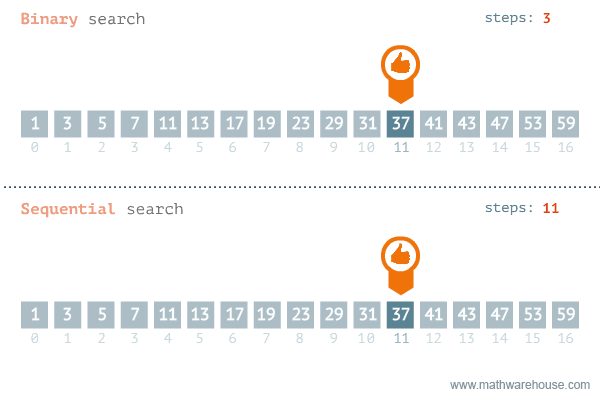
There are two ways to search for data in a list: sequential search and binary search. A sequential search is used when the items in a list are in random order; a binary search is used when the items in a list are in sorted order. Binary search is the more efficient algorithm, but you also have to take into account the extra time it takes to sort the data set before being able to search it for a value.
JavaScript has built-in functions for searching values in an array, that are the following:
- indexOf() returns the index of the value to find if the value exists otherwise returns -1.
- find() returns true if the value exists otherwise returns false.
- findIndex() return the same as indexOf.
find() and findIndex() are ES6 features and needs extra parameters to perform the search.
Sequential Search
The most obvious way to search for data in a list is to begin at the first element and move to each element in the list until you either find the data you are looking for or you reach the end of the list. This is called a sequential search, sometimes also called a linear search. It is an example of a brute-force search technique, where potentially every element in the data structure is visited on the way to a solution.
Binary Search (in linear data structures)
Binary search is used to perform a very efficient search on sorted dataset. The time complexity is O(log2N). Idea is to repeatedly divide in half the portion of the list that could contain the item, until we narrow it down to one possible item.
Some applications are:
- When you search for a name of song in a sorted list of songs, it performs binary search and string-matching to quickly return the results.
- Used to debug in git through git bisect
Searching Textual Data (in JavaScript)
breaking up the text into words using the split() function, which uses the space between each word as the delimiter. This code is not perfect because punctuation is left in the file and is stored with the nearest word, but it will suffice for our purposes. Once the textual data is stored in an array, we can begin searching through the array to find words, using Sequential or Binary Search.
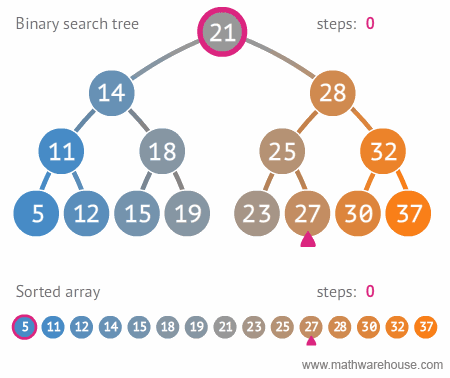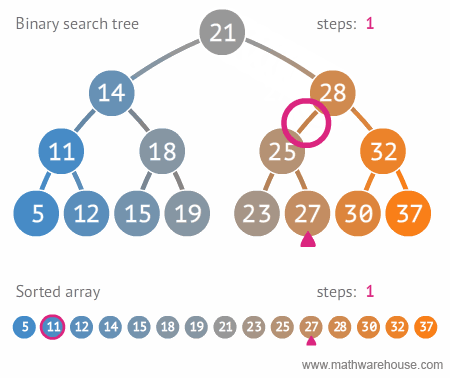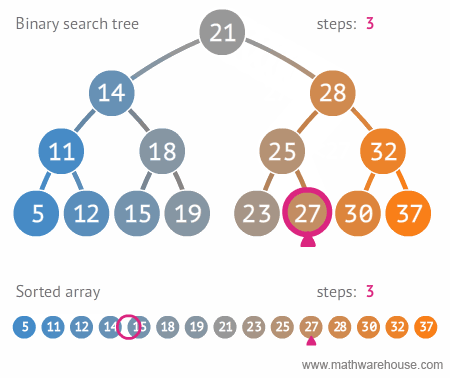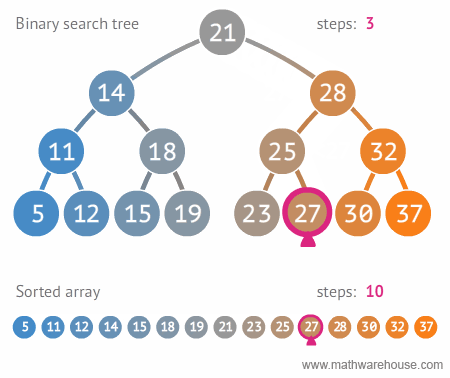
Binary Search Tree Searches
There are three types of searches typically performed with a BST:
- Searching for a specific value
- Searching for the minimum value
- Searching for the maximum value
Searches in a BST for the minimum and maximum values stored are relatively simple procedures. Since lower values are always stored in left child nodes, to find the minimum value in a BST, you only have to traverse the left edge of the BST until you get to the last node.
To find the maximum value stored in a BST, the function must simply traverse the right links of nodes until the function reaches the right end of the BST. The value stored in this node must be the maximum value.
Searching for a specific value in a BST requires that a comparison be made between the data stored in the current node and the value being searched for. The comparison will determine if the search travels to the left child node, or to the right child node if the current node doesn’t store the searched-for value.
Depth/Breadth First Search (in Graph data structures)
DFS and BFS are tree/graph traversing and searching data structures.
Determining which vertices can be reached from a specified vertex is a common activity performed on graphs. We might want to know which roads lead from one town to other towns on the map, or which flights can take us from one airport to other airports.
These operations are performed on a graph using a search algorithm. There are two fundamental searches we can perform on a graph: the depth-first search and the breadth- first search.
Applications:
- Used by search engines for web-crawling
- Used in artificial intelligence to build bots, for instance a chess bot
- Finding shortest path between two cities in a map and many other such applications