Modern business relies on multitasking to get work done. Employees are evaluated on their ability to multitask. IT professionals are routinely assigned to multiple projects. Did we always do this? Does multitasking work? What are the real impacts of multitasking? Is there an alternative?
Unitasking is a retronym to represent how we used to work on software before we multitasked. By multitask here, I really mean "work on multiple projects". Modern business has come to call that multitasking and considers it to be a strategy for more efficient worker output. We also multitask at a small scale in our daily lives, at work or not. There are similarities at both scales in how we do it and what it does to us.
When we present the Agile story to new audiences, one of the largest stumbling blocks is the idea that teams work much, much better when their members are dedicated to the team full time. This is not news. For years we have assembled "tiger teams" and "swat teams" to handle special problems, often in times of crisis. Yet our organizations have come to prefer a model of individuals in skill silos assigned to multiple projects at the same time. This is now the de-facto solution to having a large number of things to do at once. It is considered to be the most efficiently use of "scarce resources", i.e. not enough people and all of them specialized.
The Agile model turns this on its head. We form teams of people focused on a small set of things at a time. Instead of creating work and moving people through it, we create teams of people and move the work through them. And we pull instead of push.
Change is difficult. Doing things a different way takes a clear purpose, a vision of benefits and courage. So resistance is natural; people feel unsafe when things begin to change around them. If we can make a shift into Lean thinking, we can leverage two central tenants of "respect for people" and "continuously improve the system" to define a purpose, anticipate the benefits and take the first steps toward improvement. Many people hear "Lean" and think about how to be better at doing the things we are already doing. Lean also says that we can often eliminate even more waste if we stop doing some things, low-value activities, all together.
A scientist named Harold Pashler demonstrated this in the early 1990's. He called it "Dual Task Interference." Pashler theorized that there was some sort of processing bottleneck happening in a person's brain when multi-tasking. That people can really only think about one thing at a time, that a certain amount of effort was involved in packing up one process, reaching into your memory and pulling out another, and then running that job. And each time you switch tasks, that process takes time. Numerous other studies show the same thing.
A person who works on more than one project incurs a cost at each shift from one project to the other. The primary cost is the time required to change context. We know that simple interruptions like a phone call can cost as much as 15 minutes of recovery time. The more complex the task, the more time it takes to make the shift.
If you are working on more than two projects the cost can be even greater. It may have been a long time since you worked on that project, taking more effort to remember where you left off. Alternately, if you shift frequently, your context-switching time is a larger proportion of your work time.
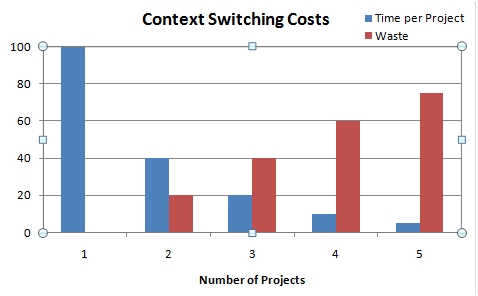
There are studies that show people are pretty good at shifting between two contexts for small tasks[3]. In a short time scale this appears to have to do with our two brain hemispheres. To a certain extent, we can parallel process two independent tasks. For larger switches, we should expect some switching cost. Jerry Weinberg[4] showed the escalating context switching costs accrued if each task has a 10% penalty, in reality the costs are frequently higher.
When a person is part of a team, either a traditional loosely connected project team or a focused Agile team, there is a compounded cost of switching. When a team member leaves to do work not related to the team's work, the team suffers from the absence of the member. When the absent member returns, the team spends time to help the returning member catch up with developments during their absence.
Let's take a tangent now to talk about the costs of context-switching (multi-tasking), which is the bane of productivity existence, at least in an Agile setting. In the 10% effort scenario above, these might include:
- Team members leave or join the team, and new members require training, knowledge transfers, or handoffs to other team members.
- Roadmap planning introduces new, even higher-priority projects, and this 10% effort project is put on hold indefinitely, or even canceled. In the last case, any partially completed work by the team would be completely wasted.
- Work that the team did on the project months earlier is forgotten so the team has to slow down to review and refresh memory. Or work done earlier becomes irrelevant because technology has been updated or changed in some way in the interim, such that rework is required.
- The team takes more time/effort to put other projects they were working on out of mind and remember what they were doing with this 10%-effort project when they last worked on it ... and repeating that cycle of forgetting/remembering every single time they switch from one project to another, as often as every single day, many times a day!
There has been a lot of research on task switching. Here's what we know from the research:
- It takes more time to get tasks completed if you switch between them than if you do them one at a time.
- You make more errors when you switch than if you do one task at a time.
- If the tasks are complex then these time and error penalties increase.
- Each task switch might waste only 1/10th of a second, but if you do a lot of switching in a day it can add up to a loss of 40% of your productivity.
- Task switching involves several parts of your brain: Brain scans during task switching show activity in four major areas: the pre-frontal cortex is involved in shifting and focusing your attention, and selecting which task to do when. The posterior parietal lobe activates rules for each task you switch to, the anterior cingulate gyrus monitors errors, and the pre-motor cortex is preparing for you to move in some way.
An Agile team is cross-functional and is busy doing all sorts of activities every day. These include elaboration of requirements, analysis, design, testing and coding. Isn't that multi-tasking? The answer has to do with the scope of context. Broad jumps in subject matter and technology require more switching time. Brains are just fine with shifting activities a little. As a focused team, all of the daily activities are targeted at a narrow band of functionality and technology. Only a few stories are being worked on at a time. The context is narrow even though the range of activities is varied. Additionally, Agile has a number of devices for keeping focus -- collaboration, task boards, automated testing, retrospection. It is the wide jumps in context that make trouble -- other projects, other collaborators, other stakeholders.
The human brain is good at internal multi-tasking. It is doing it all day long. It even does it at night. There are many parts of the brain that are working together and alone all the time. We could not function in our complex environments otherwise. Most of the multitasking is subconscious -- filtering of sensory input, integration of related information, moving data from short term to long term memory, keeping the heart and lungs going.
And we multitask externally -- driving the car while we navigate and listen to the traffic reports, talking on the phone while we make dinner, planning vacation while we are weeding the garden. Some tasks like folding laundry, walking etc. are mechanical and don't incur a task switching cost. Others like the keystrokes to navigate through a document or rename a method can be made mechanical over time. But the work of software development isn't that simple. Much of this automatic multitasking works well. It does have its limits, though
The context switching of modern multi-project assignments creates a potential for mental re-work. Human brains have two separate kinds of memory -- short term (working memory) and long term. There are mechanisms for moving information between the two. There is no guaranty that everything gets moved or that the information going in is the same that later comes back out. We are constantly editing our memories, every time we replay them. New information must reside in short term memory for a length of time before it is moved into long term memory. For example, cramming for an exam may get you a better grade but you may remember little of the material two weeks later. Simply that you may not retain the last things you worked on before the context switch. And those are likely the things you most want to know when you come back to the project.
Research suggests many ways in which multitasking is inefficient or even harmful. Consider:
- There is evidence that multitasking actually degrades short term memory, not just for the topics being multitasked but possibly by impacting areas of the brain. Multitasking creates stress; Stress invokes the more primitive parts of the brain that are concerned with personal safety, pulling energy from the more modern parts concerned with higher level thinking. Stress can also damage cells needed for new memories.
- We are more prone to errors when we multitask so the quality of our work results goes down. This, of course, adds costs to a project because things need to be fixed.
- Some parts of the brain are sequential processors, able to accept only one input at a time.
- The prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain most used for complex cognition and decision making, is the biggest energy consumer in the brain. Additional load from multitasking will lead to a quicker depletion of cognitive ability and more frequent need for recovery time.
How do we reduce the amount of multi-tasking for individuals in an Agile context? We mentioned some approaches to this earlier. A more physical environment engages more parts of the brain, leading to faster and more complete synthesis of information. A more focused effort keeps the context scope narrow. Human interactions and a Scrum Master to facilitate some of the interactions will help to keep that focus.
Some modern technical practices help improve focus for example:
- Test Driven Development ( TDD ) helps focus technical work in a narrow band for a short time
- Continuous Integration ( CI ) helps focus by giving immediate attention to a broken build or failed test
- Pair Programming ( XP ) helps two people focus on a small area of code
Arguments against multitasking have been known for a long time, yet our modern corporate culture is habituated to this form of "load balancing" for maximally efficient use of human "resources". We assemble teams of people in loose groupings of skill-providers working part time on several things at a time. Can you build a high performance team of part-time members? Or have we come to think that it is more important that everyone appear to be busy all the time?
One of the hardest parts of learning is to unlearn current behaviors. This is true for organizations as much as for individuals, it is just hard to make the mental leap from what we do now to what might work better. Here is a simple visual argument that might help guide a change that is not only easier on people, it makes good financial sense.
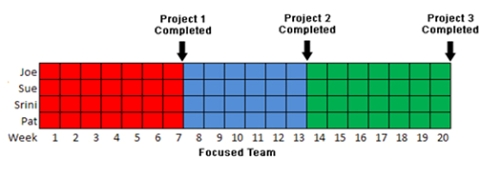
In this scenario - shown in below. Has of 4 people working on 3 short projects. The dynamics are the same for more people and larger projects. In this scenario, the people are multitasking on 4 projects.
In this scenario - shown in below. In which the same people form a single team and complete the projects sequentially. This scenario makes the very conservative assumption that there are no productivity gains from teaming or from the reduced number of context switches. Notice that all projects are completed by the same date in both scenarios but that 2 of the 3 projects finish sooner in this scenario. Imagine the resulting financial benefits.
In this scenario - show in below. With the reduction of context switching and a modest 10% gain in productivity due to teaming synergies, we would expect to see all 3 projects finish even sooner as illustrated.
References
- Infoq - Multitasking problems
- Scrum Inc - multitasking
- Scrum Inc - Alternative to kanban one piece
- Solutions IQ - agile resolution 1 destroy multi tasking the productivity killer
- Psychology Today - the true cost multi tasking
- Joel on software - human task switches considered harmful
- Linkedin - how being busy makes you less productive dr travis bradberry