| IntelliJ IDEA |
|---|
It's hard. It's always hard the first time you do something. Especially when you are collaborating, making mistakes isn't a comfortable thing. But open source is all about collaboration & working together. We wanted to simplify the way new open-source contributors learn & contribute for the first time.
Reading articles & watching tutorials can help, but what comes better than actually doing the stuff without messing up anything. This project aims at providing guidance & simplifying the way rookies make their first contribution. Remember the more relaxed you are, the better you learn. If you are looking for making your first contribution, just follow the simple steps below. We promise you, it will be fun.
If you don't have IntelliJ IDEA on your machine, install it.
Notice: This tutorial was made using IntelliJ IDEA (Version 2019.3.2) on a Windows 10 machine. Later in this tutorial we will make use of some keyboard shortcuts. These may differ on other operating systems (macOS/Linux).
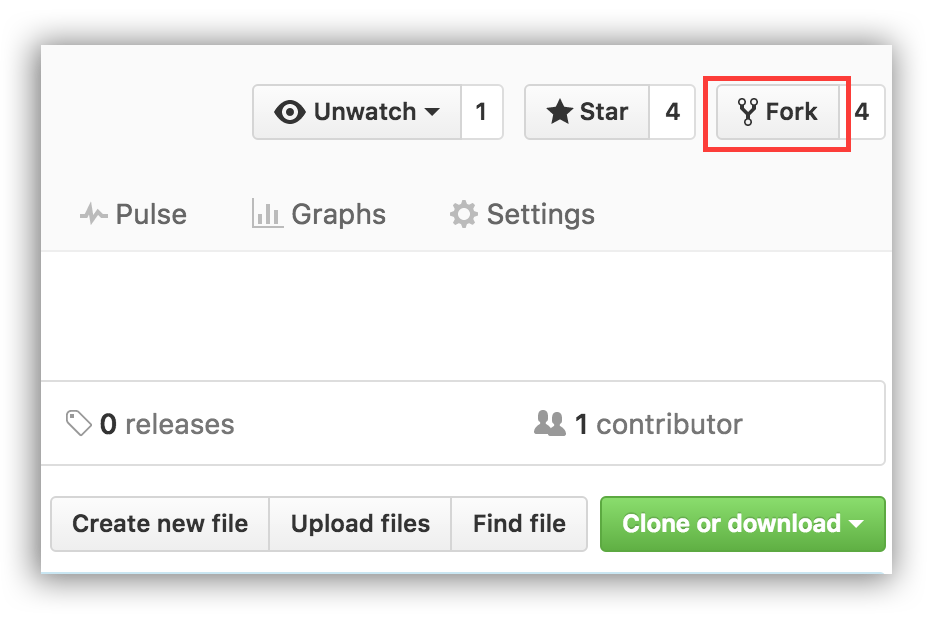
Fork this repo by clicking on the fork button on the top right of this page. This will create a copy of this repository in your GitHub account.
GitHub keeps track of the relationship between your repo and the one you have forked it from. You can think of your repo as a working copy.
Most top-level GitHub Repos (i.e. ones not forked from any other repo) have a small core team of people who can directly commit changes. All other contributors must fork the repo and make changes in the fork, then create a Pull Request to request to merge back their changes into the top-level repo. If the top-level repo administrator approves the changes they will be merged, and you will gain instant fame and fortune! More on how to do that later.
The next step is to clone your repo down to your machine so you can begin making changes. IntelliJ IDEA needs the URL of your repo, so click the "clone" button and then click the "copy to clipboard" icon.
CAREFUL: One mistake that new contributors often make is to clone the repo you forked from rather than cloning your repo. Check your browser's address bar and make sure you are cloning your repo.
Now open up IntelliJ IDEA.
IntelliJ IDEA allows you to check out (in Git terms clone) an existing repository and create a new project based on the data you've downloaded.
From the main menu, choose VCS | Get from Version Control, or, if no project is currently opened, click Get from Version Control on the Welcome screen.
In the Get from Version Control dialog, specify the URL of the remote repository you want to clone (you can click Test to make sure that connection to the remote can be established) or select one of the VCS hosting services on the left. If you are already logged in to the selected hosting service, completion will suggest the list of available repositories that you can clone.
Click Clone. If you want to create an IntelliJ IDEA project based on the sources you have cloned, click Yes in the confirmation dialog. Git root mapping will be automatically set to the project root directory.
If your project contains submodules, they will also be cloned and automatically registered as project roots.
Important: Make sure it is the forked repository and not the original one, otherwise it won't work.
In Git, branching is a powerful mechanism that allows you to diverge from the main development line, for example, when you need to work on a feature or freeze a certain state of a codebase for a release, and so on.
In IntelliJ IDEA, all operations with branches are performed in the Git Branches popup. To invoke it, click the Git widget in the Status bar or press Ctrl+Shift+`.
The name of the branch that is currently checked out is displayed in the Git widget in the Status bar.
In the Branches popup, choose New Branch.
In the dialog that opens, specify the branch name, and make sure the Checkout branch option is selected if you want to switch to that branch.
The new branch will start from the current HEAD. If you want to start a branch from a previous commit instead of the current branch HEAD, select this commit in the Log tab of the Version Control tool window Alt+9 and choose New Branch from the context menu.
Open Contributors.md and add your name anywhere in the file. This file contains GFM (GitHub Flavored Markdown) which is a proprietary flavor of the markdown syntax.
Copy one of the other contributors' lines and modify it with your name to make sure you get the syntax right - it can be picky.
Select the files you want to commit or an entire changelist in the Local Changes tab of the Version Control tool window Alt+9 and press Ctrl+K or click Commit Commit button on the toolbar.
The Commit Changes dialog that opens lists all files that have been modified since the last commit, as well as all newly added unversioned files.
Enter a meaningful commit message.
You can click Commit Message history Commit Message history Ctrl+M to choose from the list of recent commit messages.
You can also edit the commit message later before you've pushed the commit.
Press Ctrl+Shift+K or choose VCS | Git | Push from the main menu. The Push Commits dialog opens showing all Git repositories (for multi-repository projects) and listing all commits made in the current branch in each repository since the last push.
At this point you have completed your change but it still only resides in your repo. This step will show you how to submit a request to the administrator of the top-level repo to merge your change.
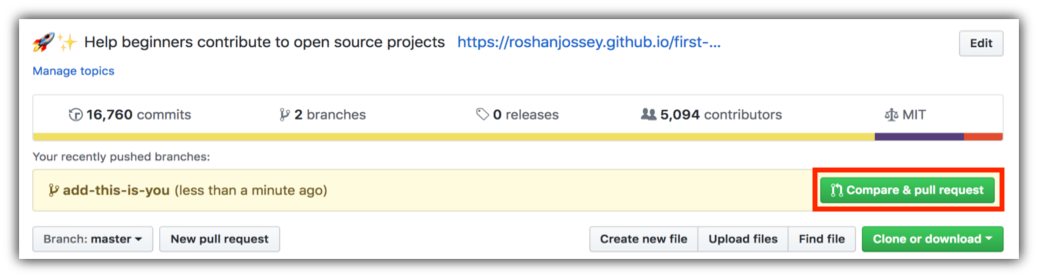
In your repo on GitHub you'll see the Compare & pull request button next to the new branch notification. Click on that button.
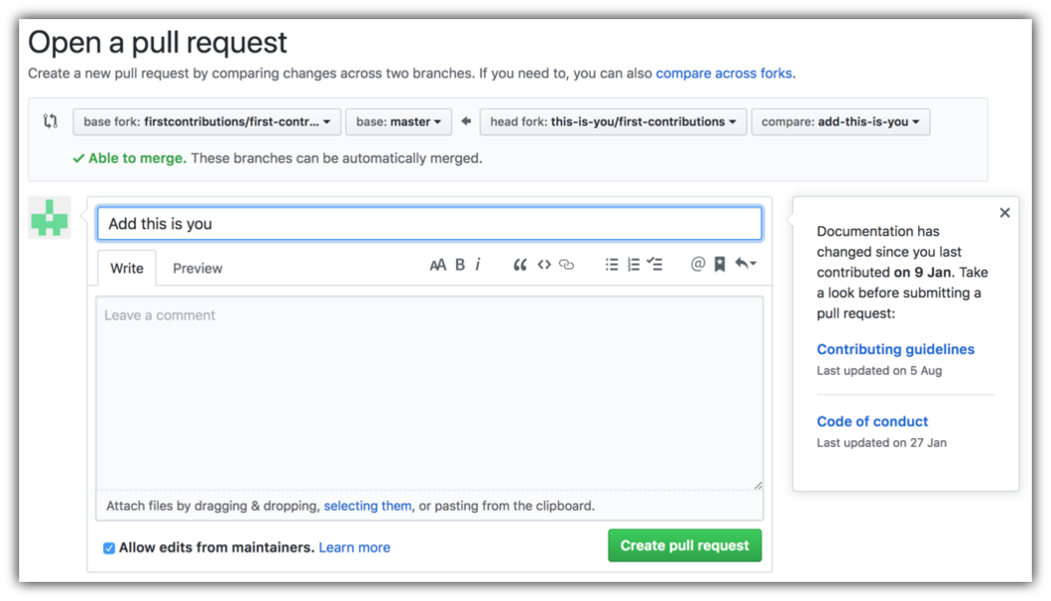
Now submit the pull request.
Soon I'll be merging all your changes into the master branch of this project. You will get a notification email once the changes have been merged.
Congrats! You have just completed the standard fork -> clone -> edit -> PR workflow that you'll encounter often as a contributor!
Celebrate your contribution and share it with your friends and followers by going to web app.
You can join our slack team in case you need any help or have any questions. Join slack team.