We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation.
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
由于这里权限是基于 Bit 的所以需要大家对位以及位操作符需要有一定的认识
位
位操作符
[TOC]
操作符速记:
&
|
^
我们以四种权限的 CRUD 来举例,使用 4 位的 bit 来进行。这里有一点需要注意,单一权限有且只有一位为 1
const curPermission = 0b1001; // 当前用户的权限,「增」「查」 const allowCreate = (curPermission & C) === C; // => true const allowUpdate = (curPermission & U) === U; // => false
从上面代码可知,当前用户的权限为Ob1001第一位与第四位是1,则说明拥有增和查的权限
Ob1001
1
增
查
当用户的权限使用按位与只有相同位都为 1 时才可以得到 1
按位与
由图与代码可以看出,我们可以使用&得到的值对比定义好的变量是否相等可知,当前是否有某个权限
let curPermission = 0b0100; // 当前用户只有「改」权限 // C = 0b0001 D = 0b0010 // 添加「增」「删」的权限 curPermission = curPermission | C | U; // => 0b0111
最终我们得到的权限包含原有的「改」以及新加入的「增」「删」
删除时我们使用先按位取反再按位与&(~P)的操作
&(~P)
let curPermission = 0b1110; // 当前用户权限,「删」「改」「查」 // R = 0b1000 curPermission = curPermission & ~C; // => Ob0110 删除了「查」的权限
最终我们得到的权限只有「删」「改」,已经将「查」权限删除
使用按位异或无则增有则减(对应位不同为 1,相同为 0),从结果来看实际上是一个 Toggle 操作
let curPermission = 0b1000; // 当前用户权限,「查」 // 无则增;C = 0b0001 curPermission ^ C; // => Ob1001 得到的为「增」「查」 // 有则减 curPermission ^ C; // => Ob1001 得到的为「查」,又将「增」权限删除了
我们可以使用复合操作来进行更方便快捷的操作,可用于上面任意操作,这里只用校验来举例
校验
当我们的页面中有下图中的操作列,既有删除按钮也就修改按钮,就出现下面几种情况:
Delete
Edit
operation
const curPermission = 0b1000; // 当前用户权限 const D = 0b0010; // 删 const U = 0b0100; // 改 const DandU = 0b0110; // 删、改 都有 const allowDelete = (p: number) => (p & D) === D; const allowUpdate = (p: number) => (p & U) === U; const allowDeleteAndUpdate = (p: number) => (p & DandU) === DandU; const COLUMNS = [ { title: 'operation', dataIndex: 'operation', render: () => ( <> {allowUpdate(curPermission) && <button>Edit</button>} {allowDelete(curPermission) && <button>Delete</button>} </> ), }, ]; const retColumns = COLUMNS.filter((x) => { if (x.dataIndex === 'operation') { return allowDeleteAndUpdate(curPermission); } return true; }); // retColumns 是我们最终使用的 Table columns 数据
同理,代码中的复合类型可以应用至其它的操作,作为作业有心的同学可以 coding
cosnt allowCreateAndUpdate = 0b1010
(curAccess & allowCreateAndUpdate) === allowCreateAndUpdate
位运算符将它的操作数视为32位元的二进制串 -- 来自 MDN
这样的话可用的权限数有限,可以使用结构体或命名空间来进行管控
结构体
命名空间
结构体也就是对象,我们将具体的权限放在定好的结构体中
const permissionList = [ { pid: 1, // position id 也就是 位置ID code: 0b0001, // 对应的编码 } ];
命名空间,其实也可以使用上面结构体描述,这里我们使用字符串来进行描述,有一套默认规则:pos,code
pos,code
const permissionList = ['pos1,0b0001', 'pos2,0b0011'];
在具体使用时根据自己的不同规则编写好对应权限的操作方法,提供给具体的业务同学使用
使用 Enum 与位赋值操作符以及 namespace 的静态方法
/** 定义 */ enum AuthCode { Read = 0b001, // 也可以写成 1 Write = 0b010, // 也可以写成 r << 1 或 2 /** 执行 execute */ Exec = 0b100, // 也可以写成 r << 2 或 4 // 以下为复合类型 /** 0b011 */ ReadAndWrite = 0b011, /** Union of all host auth */ HostAuthMask = 0b111, } namespace Auth { /** * 验证当前权限是否存在 * @param validCode - 要验证的权限编码(即用户返回的编码) * @param code - 定义好的权限编码 */ export const validator = (validCode: AuthCode, code: AuthCode): boolean => { return (validCode & code) === code; }; // curry 处理 validator() /** * 给用户加入权限 * @param userCode - 当前用户拥有的权限 * @param waitingCode - 待加入给用户的权限 * @returns 返回加入权限后的所有权限 */ export const add = ( userCode: AuthCode, waitingCode: AuthCode | AuthCode[] ): AuthCode => { let code: number; if (Array.isArray(waitingCode)) { code = waitingCode.reduce((acc, cur) => { return acc | cur; }, 0); } else { code = waitingCode; } return userCode | code; }; /** * 删除用户的权限 * @param userCode - 当前用户拥有的权限 * @param rmCode - 要删除的权限 */ export const remove = ( userCode: AuthCode, rmCode: AuthCode | AuthCode[] ): AuthCode => { let code: number; if (Array.isArray(rmCode)) { code = rmCode.reduce((acc, cur) => { return acc | cur; }, 0); } else { code = rmCode; } return userCode & ~code; }; /** * 用户权限 Toggle * @description 无则增,有则减 * @param userCode - 当前用户拥有的权限 * @param tglCode - 要 toggle 的权限 */ export const toggle = (userCode: AuthCode, tglCode: AuthCode) => { return userCode ^ tglCode; }; } // test validator // const userCode = 0b011; // 获取到用户在当前页的权限码(读、写) // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Read)); // => true; 当前用户拥有 读 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.ReadAndWrite)); // => true; 当前用户拥有 读写 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Exec)); // => false; 当前用户没有 执行 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Read | AuthCode.Exec)); // => false; 当前用户没有 读,执行 权限;两个权限都有才为真 // test add // let userCode = 0b000; // 获取到用户在当前页的权限码(无权限) // console.log((userCode = Auth.add(userCode, AuthCode.Read))); // => 1 === 0b001; 给当前用户加入 读 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Read)); // => true; 验证当前用户已经拥有 读 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Write)); // => false; 验证当前用户没有 写 权限 // console.log((userCode = Auth.add(userCode, [AuthCode.Write, AuthCode.Exec]))); // => 7 === 0b111; 给当前用户加入 写、执行 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.HostAuthMask)); // => true; 验证当前用户拥有所有权限 // test remove // let userCode = 0b111; // 获取到用户在当前页的权限码(所有权限) // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.HostAuthMask)); // => true; 验证当前用户有所用权限 // console.log((userCode = Auth.remove(userCode, AuthCode.Read))); // => 6 === 0b110; 移除用户 读 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Read)); // => false; 验证当前用户已经删除 读 权限 // console.log( // (userCode = Auth.remove(userCode, [AuthCode.Write, AuthCode.Exec])) // ); // => 0 === 0b000; 移除用户 读、执行 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Write)); // => false; 验证当前用户已经删除 写 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Exec)); // => false; 验证当前用户已经删除 执行 权限 // test toggle // let userCode = 0b101; // 获取到用户在当前页的权限码(执行、读) // console.log((userCode = Auth.toggle(userCode, AuthCode.ReadAndWrite))); // => 6 === 0b110; 当前用户删除了 读,添加了 写(写 无则增,读 有则减) // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Read)); // => false; 验证当前用户无 读 权限 // console.log(Auth.validator(userCode, AuthCode.Write)); // => true; 验证当前用户有 写 权限
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
No branches or pull requests
基于位运算的权限设计
[TOC]
前置知识
操作符速记:
&按位与:对应位都是 1 则为 1|按位或:对应位都是 0 则为 0^按位异或:对应位都相同则是 0,不同则为 1实际案例
我们以四种权限的 CRUD 来举例,使用 4 位的 bit 来进行。这里有一点需要注意,单一权限有且只有一位为 1
校验某些权限
从上面代码可知,当前用户的权限为
Ob1001第一位与第四位是1,则说明拥有增和查的权限当用户的权限使用
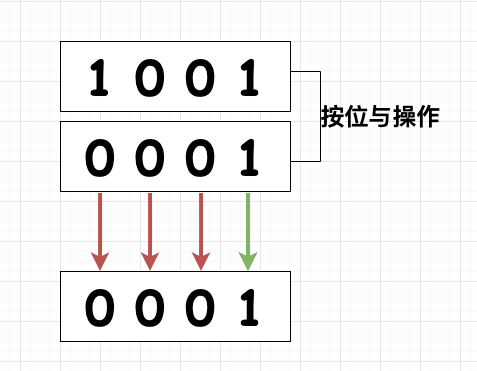
按位与只有相同位都为 1 时才可以得到 1由图与代码可以看出,我们可以使用
&得到的值对比定义好的变量是否相等可知,当前是否有某个权限添加某个权限
最终我们得到的权限包含原有的「改」以及新加入的「增」「删」
删除某个权限
删除时我们使用先按位取反再按位与
&(~P)的操作最终我们得到的权限只有「删」「改」,已经将「查」权限删除
Toggle 操作
使用按位异或无则增有则减(对应位不同为 1,相同为 0),从结果来看实际上是一个 Toggle 操作
复合类型
我们可以使用复合操作来进行更方便快捷的操作,可用于上面任意操作,这里只用
校验来举例当我们的页面中有下图中的操作列,既有删除按钮也就修改按钮,就出现下面几种情况:
Delete按钮Edit按钮operation列隐藏同理,代码中的复合类型可以应用至其它的操作,作为作业有心的同学可以 coding
优点
cosnt allowCreateAndUpdate = 0b1010,使用时(curAccess & allowCreateAndUpdate) === allowCreateAndUpdate缺点
这样的话可用的权限数有限,可以使用
结构体或命名空间来进行管控结构体也就是对象,我们将具体的权限放在定好的结构体中
命名空间,其实也可以使用上面结构体描述,这里我们使用字符串来进行描述,有一套默认规则:
pos,code在具体使用时根据自己的不同规则编写好对应权限的操作方法,提供给具体的业务同学使用
TypeScript 加成
使用 Enum 与位赋值操作符以及 namespace 的静态方法
See Also
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: