-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.1k
IPC vi VN
ASF có bao gồm giao diện IPC độc nhất của riêng nó và có thể được sử dụng để tương tác thêm với quá trình. IPC viết tắt cho inter-process communication (giao tiếp giữa các quá trình), và trong định nghĩa đơn giản nhất thì đây là "giao diện web ASF" được dựa trên máy chủ HTTP Kestrel, có thể được sử dụng để tích hợp thêm với quá trình, trong cả việc làm giao diện frontend cho người dùng (ASF-ui) và phụ trợ backend cho tích hợp bên thứ ba (ASF API).
IPC có thể được sử dụng cho rất nhiều việc khác nhau, tùy thuộc vào nhu cầu và kỹ năng của bạn. Ví dụ, bạn có thể sử dụng nó để tìm nạp trạng thái của ASF và tất cả các bot, gửi lệnh ASF, tìm nạp và chỉnh sửa cấu hình toàn bộ/bot, thêm bot mới, xóa bot hiện có, gửi khóa cho BGR hoặc truy cập tệp nhật ký của ASF. Tất cả các hành động đó đều được hiển thị bởi API của chúng tôi, có nghĩa là bạn có thể tự code các công cụ và tập lệnh của riêng mình để có thể giao tiếp với ASF và tác động đến nó trong thời gian chạy. Ngoài ra, các hành động đã chọn (chẳng hạn như gửi lệnh) cũng được thực hiện bởi ASF-ui của chúng tôi, cho phép bạn dễ dàng truy cập chúng thông qua giao diện web thân thiện.
Trừ khi bạn tắt IPC bằng cách thủ công thông qua thuộc tính cấu hình chung IPC, nó được bật theo mặc định. ASF sẽ nêu rõ việc khởi chạy IPC trong nhật ký của nó, là cái mà bạn có thể sử dụng để xác minh xem giao diện IPC đã khởi động đúng cách hay chưa:
INFO|ASF|Start() Starting IPC server...
INFO|ASF|Start() IPC server ready!
Máy chủ http của ASF hiện đang lắng nghe trên các điểm cuối đã chọn. Nếu bạn không cung cấp tệp cấu hình tùy chỉnh cho IPC, các điểm cuối đó sẽ là 127.0.0.1 dựa trên IPv4 và [::1] dựa trên IPv6 theo cổng 1242 mặc định. Bạn có thể truy cập giao diện IPC của chúng tôi bằng các liên kết trên, từ chính máy đang chạy quy trình ASF.
Giao diện IPC của ASF có ba cách khác nhau để truy cập nó, tùy thuộc vào kế hoạch sử dụng của bạn.
Ở cấp thấp nhất có ASF API là cốt lõi của giao diện IPC của chúng tôi và cho phép mọi thứ khác hoạt động. Đây là những gì bạn muốn sử dụng trong các công cụ, tiện ích và dự án của riêng bạn để giao tiếp trực tiếp với ASF.
Ở cấp bậc trung gian có tài liệu Swagger của chúng tôi, hoạt động như một giao diện người dùng frontend cho ASF API. Nó chứa một tài liệu đầy đủ về ASF API và cũng cho phép bạn truy cập nó dễ dàng hơn. Đây là những gì bạn muốn kiểm tra nếu bạn đang lên kế hoạch viết một công cụ, tiện ích hoặc các dự án khác được cho là giao tiếp với ASF thông qua API của nó.
Ở cấp độ cao nhất có ASF-ui dựa trên ASF API của chúng tôi và cung cấp cho người dùng một cách thân thiện hơn để thực thi các hành động ASF. Đây là giao diện IPC mặc định của chúng tôi được thiết kế cho người dùng cuối, và là một ví dụ hoàn hảo về những gì bạn có thể xây dựng nên với ASF API. Nếu muốn, bạn có thể sử dụng giao diện web tùy chỉnh của riêng mình để sử dụng với ASF, bằng cách chỉ định đối số dòng lệnh --path và sử dụng địa chỉ www tùy chỉnh ở đó.
ASF-ui là một dự án cộng đồng nhằm mục đích tạo ra một giao diện web đồ họa thân thiện với người dùng. Để đạt được điều đó, nó hoạt động như một giao diện người dùng cho ASF API của chúng tôi, cho phép bạn thực hiện nhiều hành động một cách dễ dàng. Đây là giao diện người dùng mặc định mà ASF đi kèm.
Như đã nêu ở trên, ASF-ui là một dự án cộng đồng không được duy trì bởi các nhà phát triển gốc của ASF. Nó tuân theo quy trình riêng của nó trong kho ASF-ui, nơi dành cho tất cả các câu hỏi, vấn đề, báo cáo lỗi và đề xuất liên quan.
You can use ASF-ui for general management of ASF process. It allows for example to manage bots, modify settings, send commands, and achieve selected other functionality normally available through ASF.
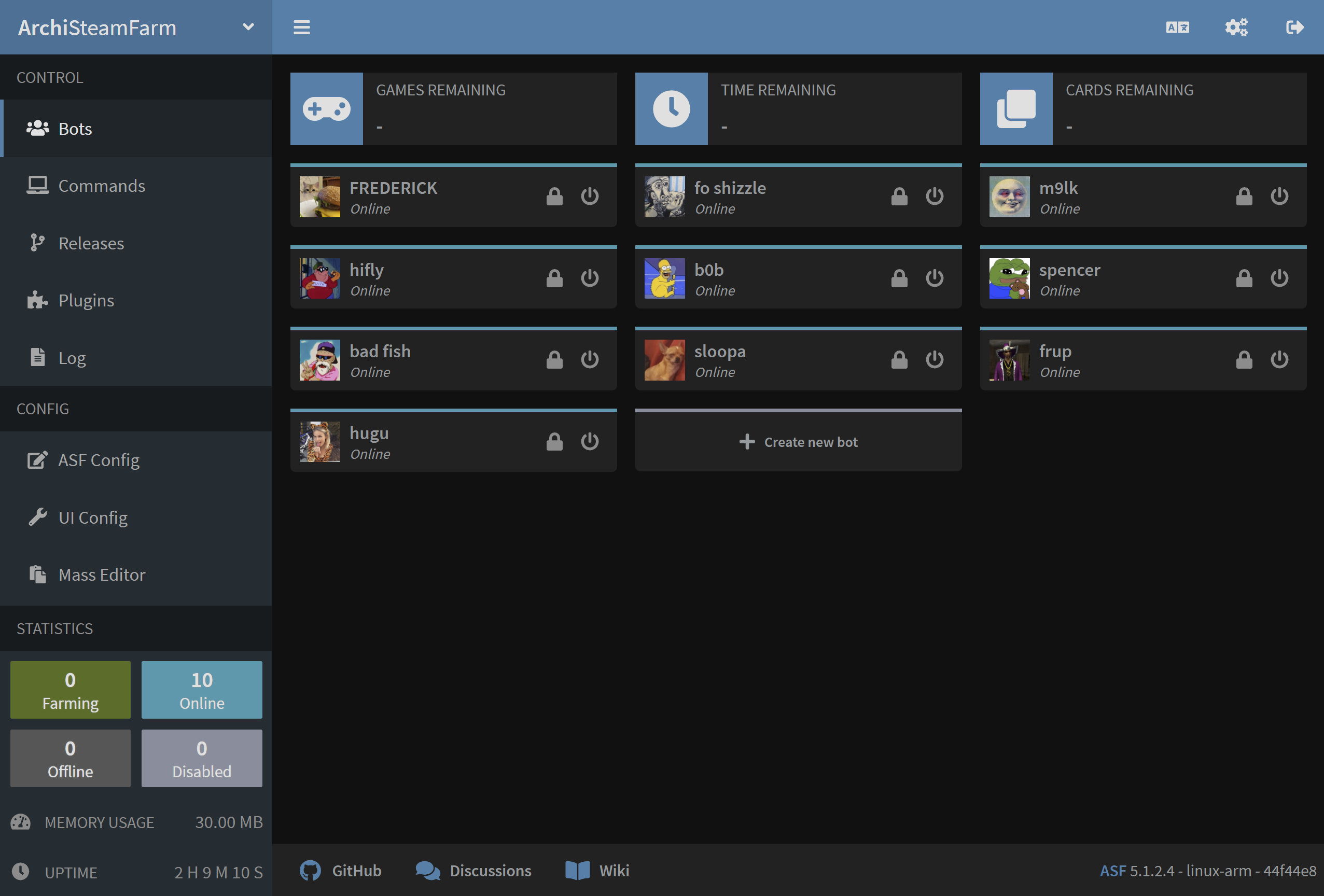
Our ASF API is typical RESTful web API that is based on JSON as its primary data format. We're doing our best to precisely describe response, using both HTTP status codes (where appropriate), as well as a response you can parse yourself in order to know whether the request succeeded, and if not, then why.
Our ASF API can be accessed by sending appropriate requests to appropriate /Api endpoints. You can use those API endpoints to make your own helper scripts, tools, GUIs and alike. This is exactly what our ASF-ui achieves under the hood, and every other tool can achieve the same. ASF API is officially supported and maintained by core ASF team.
For complete documentation of available endpoints, descriptions, requests, responses, http status codes and everything else considering ASF API, please refer to our swagger documentation.
Our IPC interface supports extra config file, IPC.config that should be put in standard ASF's config directory.
When available, this file specifies advanced configuration of ASF's Kestrel http server, together with other IPC-related tuning. Unless you have a particular need, there is no reason for you to use this file, as ASF is already using sensible defaults in this case.
The configuration file is based on following JSON structure:
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"example-http4": {
"Url": "http://127.0.0.1:1242"
},
"example-http6": {
"Url": "http://[::1]:1242"
},
"example-https4": {
"Url": "https://127.0.0.1:1242",
"Certificate": {
"Path": "/path/to/certificate.pfx",
"Password": "passwordToPfxFileAbove"
}
},
"example-https6": {
"Url": "https://[::1]:1242",
"Certificate": {
"Path": "/path/to/certificate.pfx",
"Password": "passwordToPfxFileAbove"
}
}
},
"KnownNetworks": [
"10.0.0.0/8",
"172.16.0.0/12",
"192.168.0.0/16"
],
"PathBase": "/"
}
}Endpoints - This is a collection of endpoints, each endpoint having its own unique name (like example-http4) and Url property that specifies Protocol://Host:Port listening address. By default, ASF listens on IPv4 and IPv6 http addresses, but we've added https examples for you to use, if needed. You should declare only those endpoints that you need, we've included 4 example ones above so you can edit them easier.
Host accepts either localhost, a fixed IP address of the interface it should listen on (IPv4/IPv6), or * value that binds ASF's http server to all available interfaces. Using other values like mydomain.com or 192.168.0.* acts the same as *, there is no IP filtering implemented, therefore be extremely careful when you use Host values that allow remote access. Doing so will enable access to ASF's IPC interface from other machines, which may pose a security risk. We strongly recommend to use IPCPassword (and preferably your own firewall too) at a minimum in this case.
KnownNetworks - This optional variable specifies network addresses which we consider trustworthy. By default, ASF is configured to trust loopback interface (localhost, same machine) only. This property is used in two ways. Firstly, if you omit IPCPassword, then we'll allow only machines from known networks to access ASF's API, and deny everybody else as a security measure. Secondly, this property is crucial in regards to reverse-proxies accessing ASF, as ASF will honor its headers only if the reverse-proxy server is from within known networks. Honoring the headers is crucial in regards to ASF's anti-bruteforce mechanism, as instead of banning the reverse-proxy in case of a problem, it'll ban the IP specified by the reverse-proxy as the source of the original message. Be extremely careful with the networks you specify here, as it allows a potential IP spoofing attack and unauthorized access in case the trusted machine is compromised or wrongly configured.
PathBase - This is optional base path that will be used by IPC interface. Defaults to / and shouldn't be required to modify for majority of use cases. By changing this property you'll host entire IPC interface on a custom prefix, for example http://localhost:1242/MyPrefix instead of http://localhost:1242 alone. Using custom PathBase may be wanted in combination with specific setup of a reverse proxy where you'd like to proxy a specific URL only, for example mydomain.com/ASF instead of entire mydomain.com domain. Normally that would require from you to write a rewrite rule for your web server that would map mydomain.com/ASF/Api/X -> localhost:1242/Api/X, but instead you can define a custom PathBase of /ASF and achieve easier setup of mydomain.com/ASF/Api/X -> localhost:1242/ASF/Api/X.
Unless you truly need to specify a custom base path, it's best to leave it at default.
The following config simply changes default ASF listening port from 1242 to 1337. You can pick any port you like, but we recommend 1024-32767 range, as other ports are typically registered, and may for example require root access on Linux.
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"HTTP4": {
"Url": "http://127.0.0.1:1337"
},
"HTTP6": {
"Url": "http://[::1]:1337"
}
}
}
}The following config will allow remote access from all sources, therefore you should ensure that you read and understood our security notice about that, available above.
{
"Kestrel": {
"Endpoints": {
"HTTP": {
"Url": "http://*:1242"
}
}
}
}If you do not require access from all sources, but for example your LAN only, then it's much better idea to check local IP address of the machine hosting ASF, for example 192.168.0.10 and use it instead of * in example config above.
ASF IPC interface by default does not require any sort of authentication, as IPCPassword is set to null. However, if IPCPassword is enabled by being set to any non-empty value, every call to ASF's API requires the password that matches set IPCPassword. If you omit authentication or input wrong password, you'll get 401 - Unauthorized error. After 5 failed authentication attempts (wrong password), you'll get temporarily blocked with 403 - Forbidden error.
Authentication can be done through two separate ways.
In general you should use HTTP request headers, by setting Authentication field with your password as a value. The way of doing that depends on the actual tool you're using for accessing ASF's IPC interface, for example if you're using curl then you should add -H 'Authentication: MyPassword' as a parameter. This way authentication is passed in the headers of the request, where it in fact should take place.
Alternatively you can append password parameter to the end of the URL you're about to call, for example by calling /Api/ASF?password=MyPassword instead of /Api/ASF alone. This approach is good enough, but obviously it exposes password in the open, which is not necessarily always appropriate. In addition to that it's extra argument in the query string, which complicates the look of the URL and makes it feel like it's URL-specific, while password applies to entire ASF API communication.
Both ways are supported and it's totally up to you which one you want to choose. We recommend to use HTTP headers everywhere where you can, as usage-wise it's more appropriate than query string. However, we support query string as well, mainly because of various limitations related to request headers. A good example includes lack of custom headers while initiating a websocket connection in javascript (even though it's completely valid according to the RFC). In this situation query string is the only way to authenticate.
Our IPC interface, in additon to ASF API and ASF-ui also includes swagger documentation, which is available under /swagger URL. Swagger documentation serves as a middle-man between our API implementation and other tools using it (e.g. ASF-ui). It provides a complete documentation and availability of all API endpoints in OpenAPI specification that can be easily consumed by other projects, allowing you to write and test ASF API with ease.
Apart from using our swagger documentation as a complete specification of ASF API, you can also use it as user-friendly way to execute various API endpoints, mainly those that are not implemented by ASF-ui. Since our swagger documentation is generated automatically from ASF code, you have a guarantee that the documentation will always be up-to-date with the API endpoints that your version of ASF includes.
ASF by default listens only on localhost addresses, which means that accessing ASF IPC from any other machine but your own is impossible. Unless you modify default endpoints, attacker would need a direct access to your own machine in order to access ASF's IPC, therefore it's as secure as it can be and there is no possibility of anybody else accessing it, even from your own LAN.
However, if you decide to change default localhost bind addresses to something else, then you're supposed to set proper firewall rules yourself in order to allow only authorized IPs to access ASF's IPC interface. In addition to doing that, you will need to set up IPCPassword, as ASF will refuse to let other machines access ASF API without one, which adds another layer of extra security. You may also want to run ASF's IPC interface behind a reverse proxy in this case, which is further explained below.
Yes, this is what ASF API was designed for and you can use anything capable of sending a HTTP request to access it. Local userscripts follow CORS logic, and we allow access from all origins for them (*), as long as IPCPassword is set, as an extra security measure. This allows you to execute various authenticated ASF API requests, without allowing potentially malicious scripts to do that automatically (as they'd need to know your IPCPassword to do that).
Yes, we recommend to use a reverse proxy for that. This way you can access your web server in typical way, which will then access ASF's IPC on the same machine. Alternatively, if you don't want to run with a reverse proxy, you can use custom configuration with appropriate URL for that. For example, if your machine is in a VPN with 10.8.0.1 address, then you can set http://10.8.0.1:1242 listening URL in IPC config, which would enable IPC access from within your private VPN, but not from anywhere else.
Yes, our IPC is fully compatible with such setup, so you're free to host it also in front of your own tools for extra security and compatibility, if you'd like to. In general ASF's Kestrel http server is very secure and possesses no risk when being connected directly to the internet, but putting it behind a reverse-proxy such as Apache or Nginx could provide extra functionality that wouldn't be possible to achieve otherwise, such as securing ASF's interface with a basic auth.
Example Nginx configuration can be found below. We've included full server block, although you're interested mainly in location ones. Please refer to nginx documentation if you need further explanation.
server {
listen *:443 ssl;
server_name asf.mydomain.com;
ssl_certificate /path/to/your/certificate.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/your/certificate.key;
location ~* /Api/NLog {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:1242;
# Only if you need to override default host
# proxy_set_header Host 127.0.0.1;
# X-headers should always be specified when proxying requests to ASF
# They're crucial for proper identification of original IP, allowing ASF to e.g. ban the actual offenders instead of your nginx server
# Specifying them allows ASF to properly resolve IP addresses of users making requests - making nginx work as a reverse proxy
# Not specifying them will cause ASF to treat your nginx as the client - nginx will act as a traditional proxy in this case
# If you're unable to host nginx service on the same machine as ASF, you most likely want to set KnownNetworks appropriately in addition to those
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host:$server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
# We add those 3 extra options for websockets proxying, see https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/websocket.html
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "Upgrade";
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:1242;
# Only if you need to override default host
# proxy_set_header Host 127.0.0.1;
# X-headers should always be specified when proxying requests to ASF
# They're crucial for proper identification of original IP, allowing ASF to e.g. ban the actual offenders instead of your nginx server
# Specifying them allows ASF to properly resolve IP addresses of users making requests - making nginx work as a reverse proxy
# Not specifying them will cause ASF to treat your nginx as the client - nginx will act as a traditional proxy in this case
# If you're unable to host nginx service on the same machine as ASF, you most likely want to set KnownNetworks appropriately in addition to those
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $host:$server_port;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Server $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
}
}Example Apache configuration can be found below. Please refer to apache documentation if you need further explanation.
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName asf.mydomain.com
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile /path/to/your/fullchain.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /path/to/your/privkey.pem
# TODO: Apache can't do case-insensitive matching properly, so we hardcode two most commonly used cases
ProxyPass "/api/nlog" "ws://127.0.0.1:1242/api/nlog"
ProxyPass "/Api/NLog" "ws://127.0.0.1:1242/Api/NLog"
ProxyPass "/" "http://127.0.0.1:1242/"
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>Yes, you can achieve it through two different ways. A recommended way would be to use a reverse proxy for that, where you can access your web server through https like usual, and connect through it with ASF's IPC interface on the same machine. This way your traffic is fully encrypted and you don't need to modify IPC in any way to support such setup.
Second way includes specifying a custom config for ASF's IPC interface where you can enable https endpoint and provide appropriate certificate directly to our Kestrel http server. This way is recommended if you're not running any other web server and don't want to run one exclusively for ASF. Otherwise, it's much easier to achieve a satisfying setup by using a reverse proxy mechanism.
Starting with ASF V5.1.2.1, we've added additional security measure that, by default, allows only loopback interface (localhost, your own machine) to access ASF API without IPCPassword set in the config. This is because using IPCPassword should be a minimum security measure set by everybody who decides to expose ASF interface further. You're still able to override this decision by specifying the networks which you trust to reach ASF without IPCPassword specified, you can set those in KnownNetworks property in custom config. However, unless you really know what you're doing and fully understand the risks, you should instead use IPCPassword as declaring KnownNetworks will allow everybody from those networks to access ASF API unconditionally.
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
- 🏡 Trang chủ
- 🔧 Cấu hình
- 💬 Câu hỏi thường gặp
- ⚙️ Thiết lập (bắt đầu tại đây)
- 👥 Công cụ kích hoạt trò chơi trong nền
- 📢 Lệnh
- 🛠️ Khả năng tương thích
- 🧩 ItemsMatcherPlugin
- 📋 Quản lý
- ⏱️ Hiệu năng
- 📡 Liên lạc từ xa
- 👪 Chia sẻ Gia đình Steam
- 🔄 Trao đổi

