-
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 71
Custom Scraper
This page introduce how to setup your custom scraper.
My research topic is computer vision, which is only one piece of puzzle of the computer science. If the builtin metadata scrapers are not suitable for your research, you can write your own metadata scraper.
A metadata scraper consists of three main functions: preProcess, parsingProcess, and scrapeImpl. The return values of the preProcess function usually are three elements: scrapeURL, headers, enable. parsingProcess parses the response of the database API url scrapeURL and assigns metadata to a paper entity draft: paperEntityDraft. This paperEntityDraft will go through all enabled scrapers and finally be inserted or updated to the Paperlib database. scrapeImpl firstly calls the preProcess, then does the network requesting, and finally calls the parsingProcess.
Open the preference window, click the scrapers tab, click the + button.
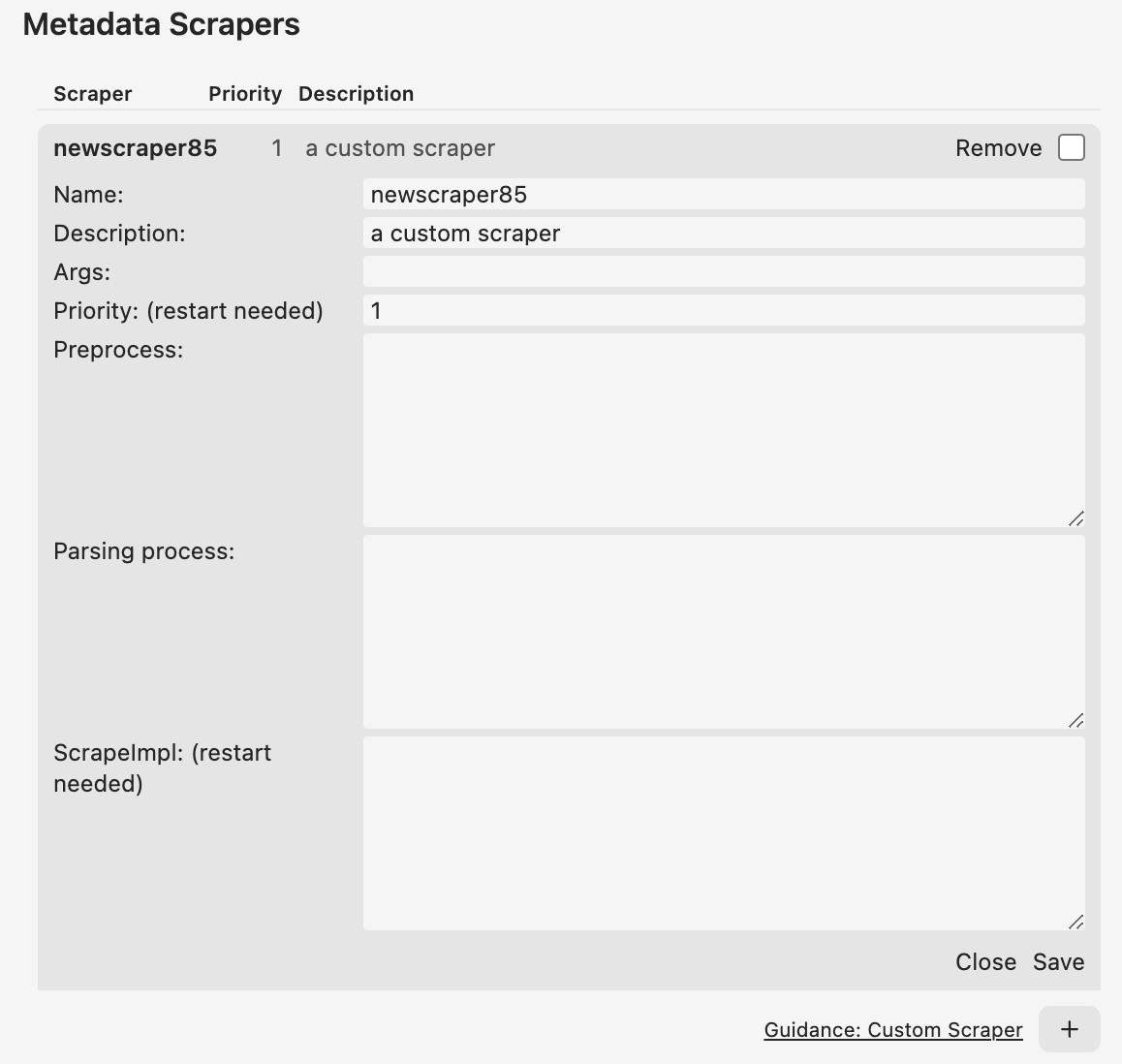
The default scrapeImpl function is:
const { scrapeURL, headers, enable } = this.preProcess(
paperEntityDraft
);
if (enable || force) {
const response = (await window.networkTool.get(
scrapeURL,
headers
));
return this.parsingProcess(response, paperEntityDraft);
} else {
return paperEntityDraft;
}Usually, it is unnecessary to modify this function.
Let's use the built-in DOI scraper as an example.
const enable =
paperEntityDraft.doi !== "" &&
this.getEnable("doi") &&
this.isPreprint(paperEntityDraft);
const doiID = formatString({
str: paperEntityDraft.doi,
removeNewline: true,
removeWhite: true,
});
const scrapeURL = `https://dx.doi.org/${doiID}`;
const headers = {
Accept: "application/json",
};
if (enable) {
this.stateStore.logState.processLog = `Scraping metadata by DOI ...`;
}
return { scrapeURL, headers, enable };This function firstly determines whether this scraper should be enabled or not. Here, if the paperEntityDraft has a valid doi property, you enabled this scraper in the preference window, and this is a preprint paper. the enable would be true.
After that, we construct the scrapeURL.
Some API requires specific HTTP header, then we set it.
Finally, we send a message to Paperlib that your scraper are going to scrape the metadata of this paper.
const response = JSON.parse(rawResponse.body)
const title = response.title;
const authors = response.author
.map((author) => {
return author.given.trim() + " " + author.family.trim();
})
.join(", ");
const pubTime = response.published["date-parts"]["0"][0];
let pubType;
if (response.type == "proceedings-article") {
pubType = 1;
} else if (response.type == "journal-article") {
pubType = 0;
} else {
pubType = 2;
}
const publication = response["container-title"];
paperEntityDraft.setValue("title", title);
paperEntityDraft.setValue("authors", authors);
paperEntityDraft.setValue("pubTime", `${pubTime}`);
paperEntityDraft.setValue("pubType", pubType);
paperEntityDraft.setValue("publication", publication);
if (response.volume) {
paperEntityDraft.setValue("volume", response.volume);
}
if (response.issue) {
paperEntityDraft.setValue("number", response.issue);
}
if (response.page) {
paperEntityDraft.setValue("pages", response.page);
}
if (response.publisher) {
paperEntityDraft.setValue(
"publisher",
response.publisher ===
"Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)"
? "IEEE"
: response.publisher
);
}
return paperEntityDraft;The parsingProcess is very easy to understand. It just parses the rawResponse and assign corresponding values to the paperEntityDraft.
Here you can use console.log(rawResponse) and console.log(paperEntityDraft) in this function to output the structure of these to input variables. You can find the log in the developer tools window (option+cmd+I).
You may need some configurable args in your scraper. For example, some database APIs, such as the IEEE xplore, may require a APIkey. Here, you can access the args in your configuration as:
const ieeeAPIKey = (this.preference.get("scrapers")["ieee"]?.args ?? "";This section introduces how to use the custom scraper feature to implement a auto tagger to automatically tag your newly-imported papers.

auto-tagger
{"semi-supervised":"semi-supervised", "segmentation":"segmentation", "detection":"detection"}
You can define your own rules: {"keywords":"tag name"}
enable = paperEntityDraft.tags.length === 0 && this.getEnable("auto-tagger");const tagMap = JSON.parse(this.preference.get("scrapers")["auto-tagger"].args);
const title = paperEntityDraft.title.toLowerCase();
let autoTags = []
for (const [key, tag] of Object.entries(tagMap)) {
if (title.includes(key.toLowerCase())) {
autoTags.push(new PaperTag(tag, 1))
}
}
paperEntityDraft.setValue("tags", autoTags);const { scrapeURL, headers, enable } = this.preProcess(
paperEntityDraft
);
if (enable) {
return this.parsingProcess('', paperEntityDraft);
} else {
return paperEntityDraft;
}