#! https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/521905931
Most of the early models focused on estimating the magnitude of spectrum while ignoring the phase.
The encoder-decoder structure in Deep Complex U-net (DCU) has been proven to be effective for complex-valued data.
Design the FDCU, which could process mag info and phase info separately through one-encoder-two-decoders structure.
Our model incorporated the masking and mapping based method to estimate clean waves from noisy.
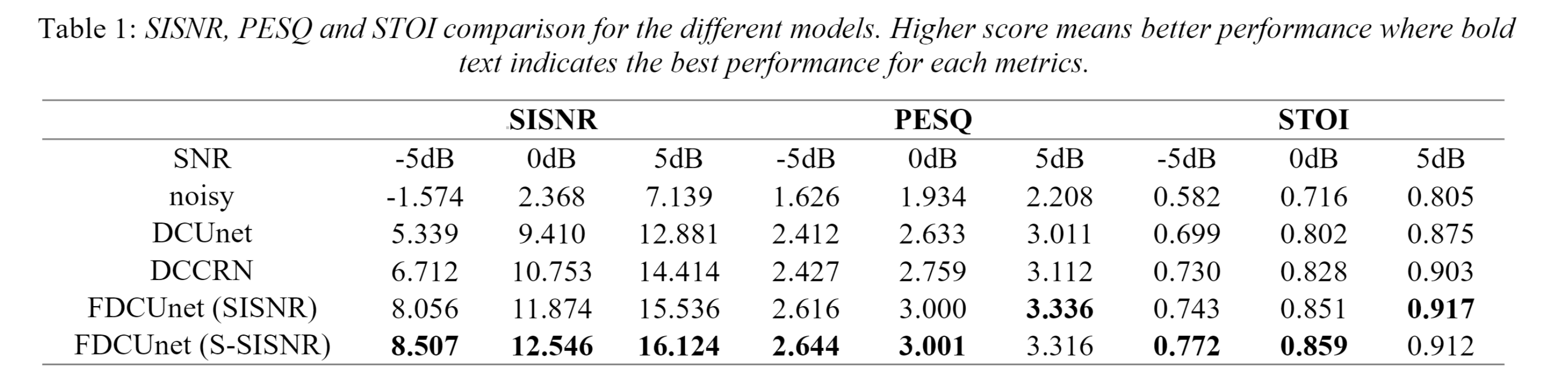
Designed a new loss func S-SISNR, which can further improve the performance of the model at low SNR.
In CASA, the concept of time-frequency mask was proposed, which inspired speech enhancement being formulated as a supervised learning problem.
Most of the early DNN-based models used T-F representations of speech signals as the input features and focused on estimating the magnitude spectrogram regardless of estimation for phase spectrogram, then used the noisy phase to reconstruct the waveform.
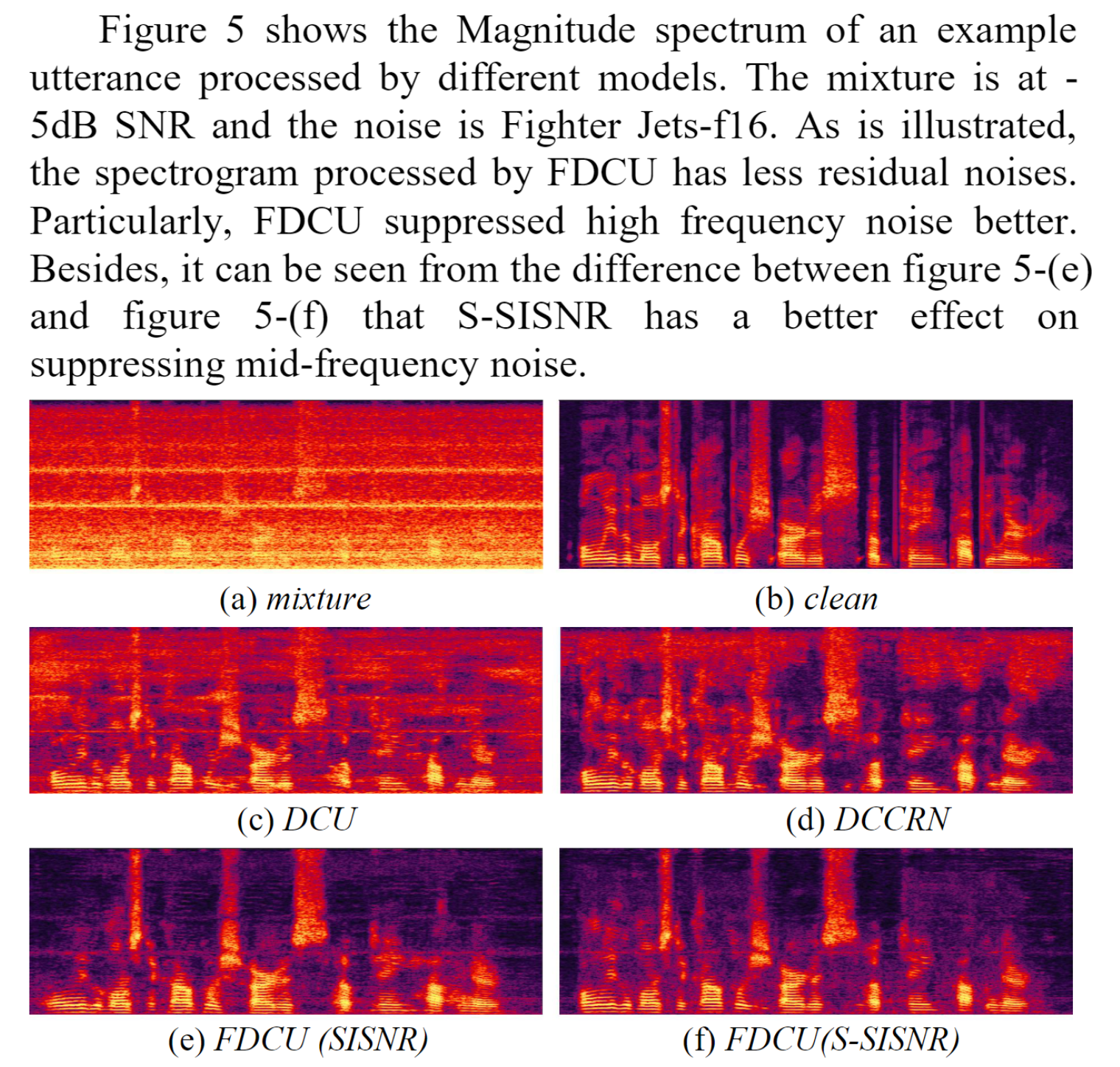
As the SNR decreases, the influence of phase becomes more and more obvious.
DNN based speech enhancement researches are mainly divided into two directions: mapping-based method and masking-based method. IBM, IRM and spectral magnitude mask (SMM) only contributes to estimate the magnitude, the emergence of phase-sensitive mask (PSM) made it possible to incorporate phase information. CRM was developed to jointly estimate real and imaginary components.
In order to obtain more accurate phase information, researchers proposed end-to-end methods, which take a encoder-separator-decoder structure while the encoder and decoder are similar to but differ from STFT and iSTFT. The separator is between the encoder and decoder, usually adopts a structure that could capture the long-range temporal sequence information. These methods work directly on time domain signals, avoiding the degradation of speech quality caused by inaccurate phase estimation in the spectral domain.
We proposed a method of using complex neural networks for speech enhancement in the T-F domain. Designed Funnel Deep Complex U-net (FDCU), which jointly applies the masking-based method and the mapping-based method for the first time. In our model, we get estimated magnitude spectrogram by IRM and directly map the noisy complex spectrum to estimate phase spectrogram. Proposed Stretched-Scale-Invariant-SNR (S-SISNR), which performs better than SISNR at low SNR.
DCU is a simple complex encoder-decoder structure with skip connection. In DCCRN, a complex LSTM layer is inserted between the encoder and the decoder. DCCRN could better model the temporal dependencies.
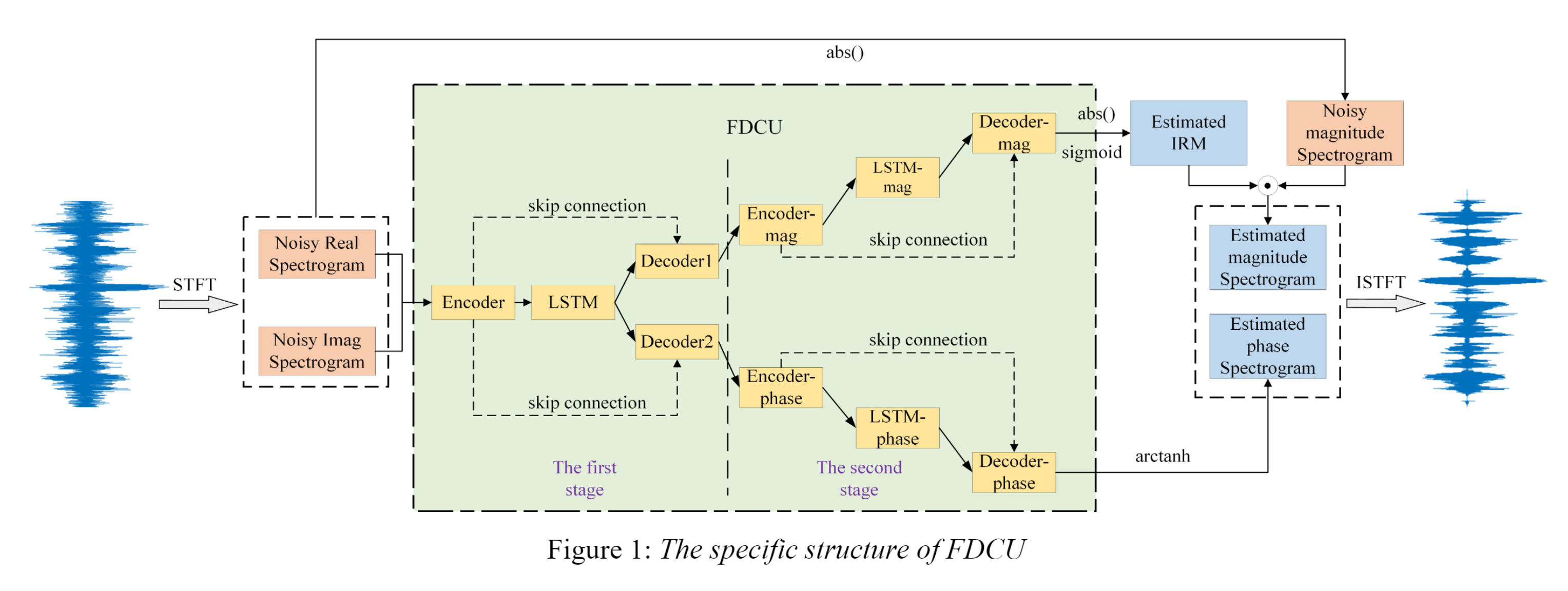
The input is the complex STFT spectrogram.
The first stage of the network is a one-encoder-two-decoders structure, and the outputs of the two decoders are both complex values, respectively model the magnitude and the phase spectrogram.
In the second stage, we connect an encoder-decoder structure after each decoder of the first stage. There are two paths in the second stage, the magnitude-path and the phase-path.
In mag-path, we use masking-based method to calculate the mag from the complex output, and get IRM matrix through the sigmoid function. $$ I \hat{R} M=\operatorname{sigmoid}\left(\sqrt{M a g_{\text {real }}^{2}+M a g_{\text {imag }}^{2}}\right) $$
In the phase-path, we directly map the complex spectrum of the noisy speech to the phase spectrum of the clean speech.
$$
\hat{P}=\operatorname{arctanh}\left(\frac{\text { Phase }{\text {imag }}}{\text { Phase }{\text {real }}}\right)
$$
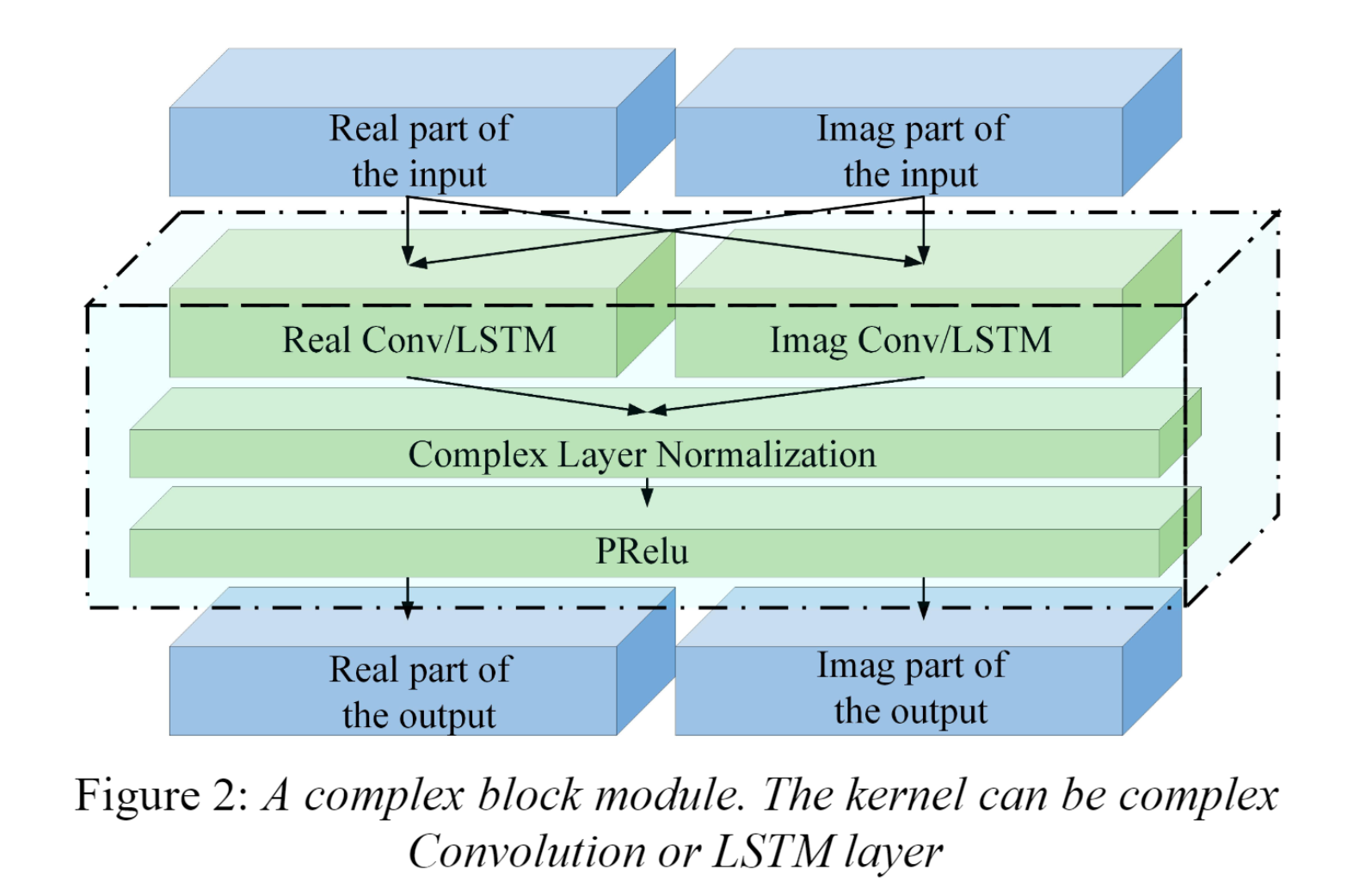 Each block consists of complex Conv2d, complex layer normalization and PRelu.
Each block consists of complex Conv2d, complex layer normalization and PRelu.
The target is to estimate the IRM and the phase spectrum.
The loss function
$$ \begin{gathered} s_{\text {target }}=<\hat{s}, s>s /|s|^{2} \ e_{\text {noise }}=\hat{s}-S_{\text {target }} \ \mathrm{SISNR}=10 \log {10} \frac{\left|s{\text {targ et }}\right|^{2}}{\left|e_{\text {noise }}\right|^{2}} \end{gathered} $$
16kHZ
Hanning window with 1024 and 256