We are given a binary tree (with root node root), a target node, and an integer value K.
Return a list of the values of all nodes that have a distance K from the target node. The answer can be returned in any order.
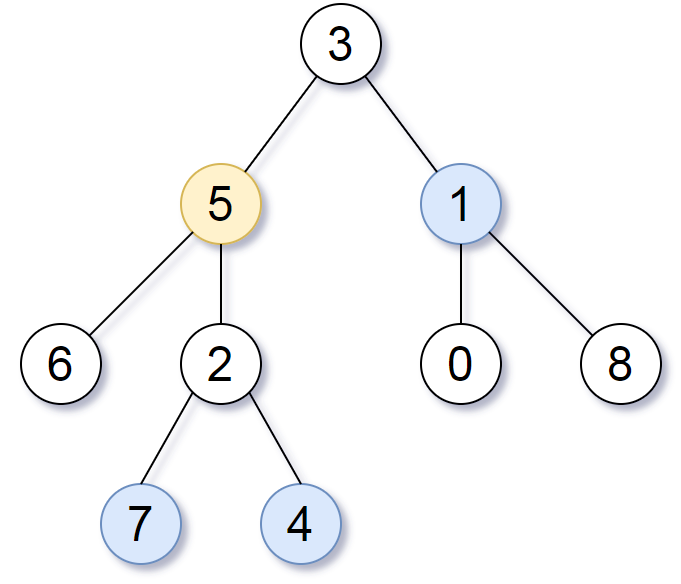
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2
Output: [7,4,1]
Explanation:
The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5)
have values 7, 4, and 1.
Note that the inputs "root" and "target" are actually TreeNodes.
The descriptions of the inputs above are just serializations of these objects.
- The given tree is non-empty.
- Each node in the tree has unique values
0 <= node.val <= 500. - The
targetnode is a node in the tree. 0 <= K <= 1000.
- mine
-
Java
Runtime: 12 ms, faster than 37.40%, Memory Usage: 39.4 MB, less than 5.26% of Java online submissionspublic Map<Integer, List<TreeNode>> map; public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) { LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>(); if (K == 0) { res.add(target.val); return res; } map = new HashMap<>(); // key is each node, and value is a list which is connected the node initMap(root, null); //record the node is used int[] record = new int[501]; //get the connected node List<TreeNode> nodes = map.get(target.val); //mark this node was used record[target.val] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) { record[nodes.get(i).val] = 1; } // if K > 1 , we need to get the while (K > 1) { List<TreeNode> temp = new LinkedList<>(); K--; for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) { //get the connected nodes List<TreeNode> t = map.get(nodes.get(i).val); for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); j++) { int val = t.get(j).val; if (record[val] != 1) { //if node is not used, save it to get next connected node. record[val] = 1; temp.add(t.get(j)); } } } nodes = temp; } for (int i = 0; i < nodes.size(); i++) { res.add(nodes.get(i).val); } return res; } public void initMap(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent) { if (node == null) { return; } List<TreeNode> t = map.getOrDefault(node.val, new ArrayList<>(3)); if (parent != null) { t.add(parent); } if (node.left != null) { t.add(node.left); } if (node.right != null) { t.add(node.right); } map.put(node.val, t); initMap(node.left, node); initMap(node.right, node); }
-
-
the most votes
Runtime: 10 ms, faster than 86.42%, Memory Usage: 39.6 MB, less than 5.26% of Java online submissionsMap<TreeNode, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) { List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>(); find(root, target); dfs(root, target, K, map.get(root), res); return res; } // find target node first and store the distance in that path that we could use it later directly private int find(TreeNode root, TreeNode target) { if (root == null) return -1; if (root == target) { map.put(root, 0); return 0; } int left = find(root.left, target); if (left >= 0) { map.put(root, left + 1); return left + 1; } int right = find(root.right, target); if (right >= 0) { map.put(root, right + 1); return right + 1; } return -1; } private void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K, int length, List<Integer> res) { if (root == null) return; if (map.containsKey(root)) length = map.get(root); if (length == K) res.add(root.val); dfs(root.left, target, K, length + 1, res); dfs(root.right, target, K, length + 1, res); }
-
the leetcode's solution
Runtime: 9 ms, faster than 100.00%, Memory Usage: 39.1 MB, less than 5.26% of Java online submissionsList<Integer> ans; TreeNode target; int K; public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int K) { ans = new LinkedList(); this.target = target; this.K = K; dfs(root); return ans; } // Return vertex distance from node to target if exists, else -1 // Vertex distance: the number of vertices on the path from node to target public int dfs(TreeNode node) { if (node == null) return -1; else if (node == target) { subtree_add(node, 0); return 1; } else { int L = dfs(node.left), R = dfs(node.right); if (L != -1) { if (L == K) ans.add(node.val); subtree_add(node.right, L + 1); return L + 1; } else if (R != -1) { if (R == K) ans.add(node.val); subtree_add(node.left, R + 1); return R + 1; } else { return -1; } } } // Add all nodes 'K - dist' from the node to answer. public void subtree_add(TreeNode node, int dist) { if (node == null) return; if (dist == K) ans.add(node.val); else { subtree_add(node.left, dist + 1); subtree_add(node.right, dist + 1); } }