leetcode Daily Challenge on October 13th, 2020.
leetcode-cn Daily Challenge on November 21th, 2020.
Difficulty : Medium
Related Topics : LinkedList、Sort
Given the
headof a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.Follow up: Can you sort the linked list in
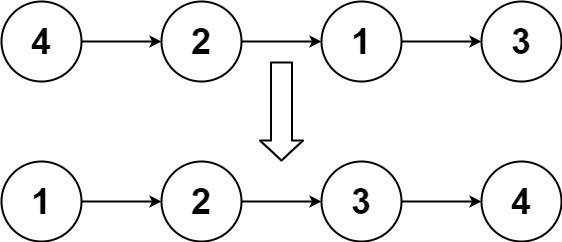
O(n logn)time andO(1)memory (i.e. constant space)?Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]Input: head = [] Output: []
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 10^4].-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
- mine
- Java
- Merge Sort
Runtime: 8 ms, faster than 25.65%, Memory Usage: 42 MB, less than 5.08% of Java online submissions//O(N * logN)time //O(logN)space public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if(head == null) return head; LinkedList<Integer> count = new LinkedList<>(); LinkedList<ListNode> list = new LinkedList<>(); while(head != null){ ListNode node = head; head = head.next; node.next = null; if(count.isEmpty() || count.getLast() != 1){ count.add(1); list.add(node); }else{ list.add(meger(list.removeLast(), node)); count.removeLast(); count.add(2); check(count, list, true); } } check(count, list, false); return list.removeFirst(); } ListNode meger(ListNode p, ListNode q) { ListNode node = new ListNode(); ListNode t = node; while (p != null || q != null) { if (p == null || q == null) { t.next = q == null ? p : q; break; } else { if (p.val > q.val) { t.next = q; q = q.next; } else { t.next = p; p = p.next; } t = t.next; } } return node.next; } void check(LinkedList<Integer> count, LinkedList<ListNode> list, boolean same){ if(count.size() < 2) return; while(count.size() > 1){ int f = count.removeLast(); int s = count.removeLast(); if(same && f != s){ count.add(s); count.add(f); break; } count.add(f + s); list.add(meger(list.removeLast(), list.removeLast())); } }
- Merge Sort
- Java
- the most votes
Runtime: 3 ms, faster than 97.49%, Memory Usage: 41 MB, less than 5.08% of Java online submissions// O(N*logN)time // O(logN)space public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; // step 1. cut the list to two halves ListNode prev = null, slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { prev = slow; slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; } prev.next = null; // step 2. sort each half ListNode l1 = sortList(head); ListNode l2 = sortList(slow); // step 3. merge l1 and l2 return merge(l1, l2); } ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode l = new ListNode(0), p = l; while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { if (l1.val < l2.val) { p.next = l1; l1 = l1.next; } else { p.next = l2; l2 = l2.next; } p = p.next; } if (l1 != null) p.next = l1; if (l2 != null) p.next = l2; return l.next; }
Top Down Merge Sort
Runtime: 3 ms, faster than 97.49%, Memory Usage: 40.9 MB, less than 5.08% of Java online submissions// O(N*logN)time // O(logN)space public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; ListNode mid = getMid(head); ListNode left = sortList(head); ListNode right = sortList(mid); return merge(left, right); } ListNode merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); ListNode tail = dummyHead; while (list1 != null && list2 != null) { if (list1.val < list2.val) { tail.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; tail = tail.next; } else { tail.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; tail = tail.next; } } tail.next = (list1 != null) ? list1 : list2; return dummyHead.next; } ListNode getMid(ListNode head) { ListNode midPrev = null; while (head != null && head.next != null) { midPrev = (midPrev == null) ? head : midPrev.next; head = head.next.next; } ListNode mid = midPrev.next; midPrev.next = null; return mid; }Bottom Up Merge Sort
Runtime: 5 ms, faster than 49.36%, Memory Usage: 41 MB, less than 5.08% of Java online submissions// O(N*logN)time // O(1)space ListNode tail = new ListNode(); ListNode nextSubList = new ListNode(); public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; int n = getCount(head); ListNode start = head; ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); for (int size = 1; size < n; size = size * 2) { tail = dummyHead; while (start != null) { if (start.next == null) { tail.next = start; break; } ListNode mid = split(start, size); merge(start, mid); start = nextSubList; } start = dummyHead.next; } return dummyHead.next; } ListNode split(ListNode start, int size) { ListNode midPrev = start; ListNode end = start.next; //use fast and slow approach to find middle and end of second linked list for (int index = 1; index < size && (midPrev.next != null || end.next != null); index++) { if (end.next != null) { end = (end.next.next != null) ? end.next.next : end.next; } if (midPrev.next != null) { midPrev = midPrev.next; } } ListNode mid = midPrev.next; midPrev.next = null; nextSubList = end.next; end.next = null; // return the start of second linked list return mid; } void merge(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(); ListNode newTail = dummyHead; while (list1 != null && list2 != null) { if (list1.val < list2.val) { newTail.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; newTail = newTail.next; } else { newTail.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; newTail = newTail.next; } } newTail.next = (list1 != null) ? list1 : list2; // traverse till the end of merged list to get the newTail while (newTail.next != null) { newTail = newTail.next; } // link the old tail with the head of merged list tail.next = dummyHead.next; // update the old tail to the new tail of merged list tail = newTail; } int getCount(ListNode head) { int cnt = 0; ListNode ptr = head; while (ptr != null) { ptr = ptr.next; cnt++; } return cnt; }